Moment of Inertia of a Disk plus YouTube
The rotational inertia of a composite object is the sum of the rotational inertias of each component, all calculated about the same axis. Itotal = I1 +I2 +I3 +. (7.4.7) (7.4.7) I t o t a l = I 1 + I 2 + I 3 +.. So for a ring and a disk stacked upon each other and rotating about the symmetry axis of both, the rotational inertia is:

Simple trick to understand Moment of Inertia of a Thin Disk. JEE
For a single particle rotating around a fixed axis, this is straightforward to calculate. We can relate the angular velocity to the magnitude of the translational velocity using the relation vt = ωr v t = ω r, where r is the distance of the particle from the axis of rotation and vt v t is its tangential speed.

ExampleInertia of disc with point masses YouTube
moment of inertia is different along the different axes. Equipment Rotational dynamics apparatus, mass set, mass hanger, block mass, caliper, pulley, smart cart, ruler. Theory The set up of the rotational apparatus consists of the disk mounted on top of a rotational vertical axis. Its angular acceleration α is caused by the tension in a
Determine The Moment Of Inertia Of A Plane Circular Disc (i) About An
Axis through center, in plane of plate. Thin Rod. Axis through mid point. Thin Rod. Axis at one end. Moment of Inertia - Rotational inertia for uniform objects with various geometrical shapes.
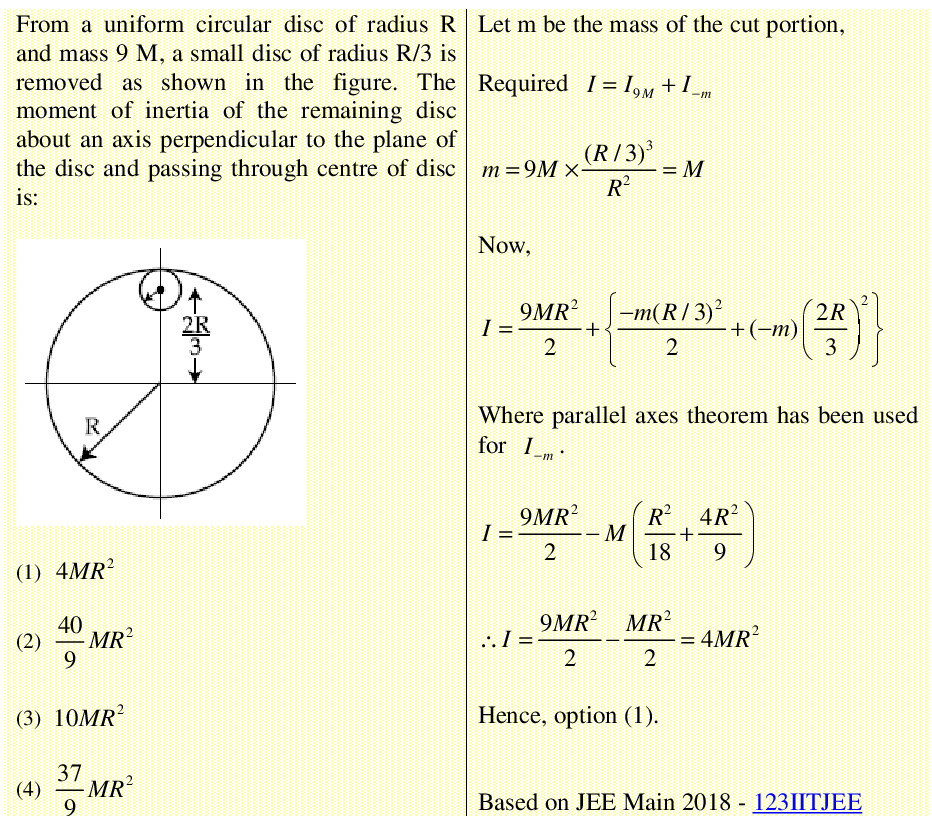
JEE Main 2018 Moment of Inertia of Disc With Circular Hole 123IITJEE
This last equation is the rotational analog of Newton's second law (F=ma), where torque is analogous to force, angular acceleration is analogous to translational acceleration, and mr 2 is analogous to mass (or inertia).The quantity mr 2 is called the rotational inertia or moment of inertia of a point mass m a distance r from the center of rotation.. Figure 2.

Experiment 1 Moment of Inertia PHYSICS LAB A12 GROUP2
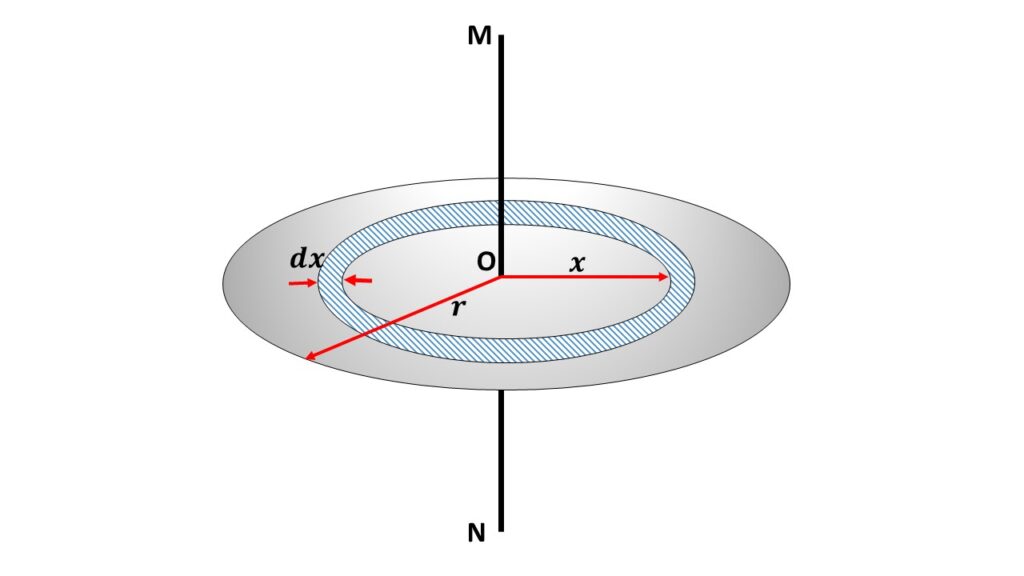
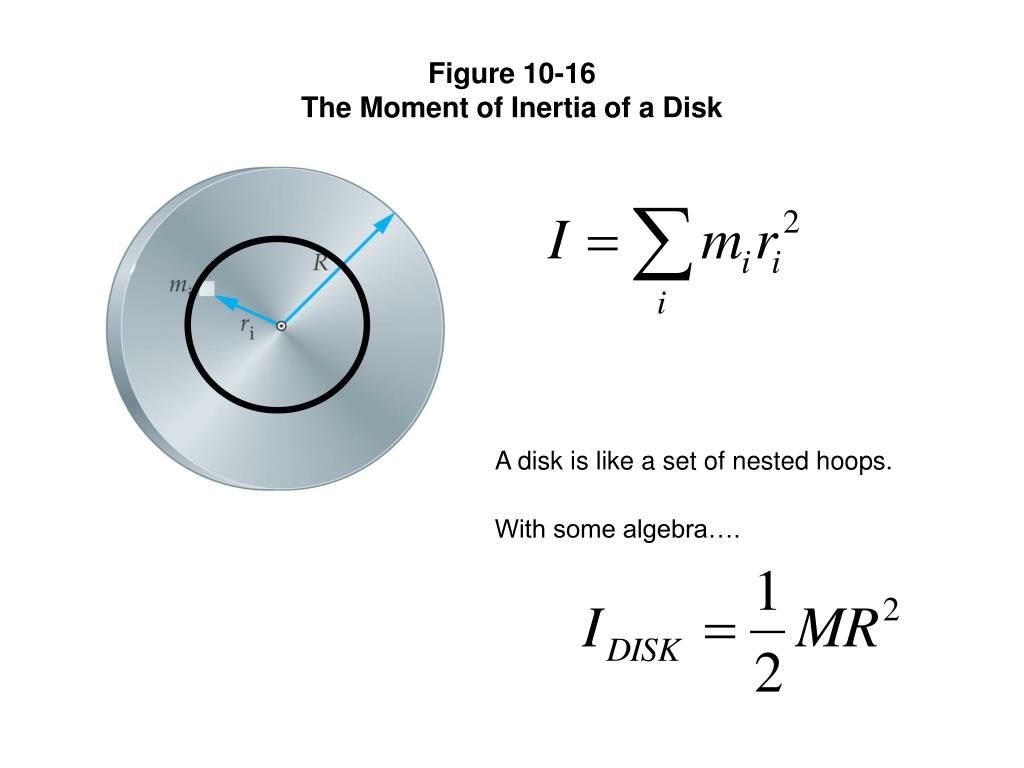
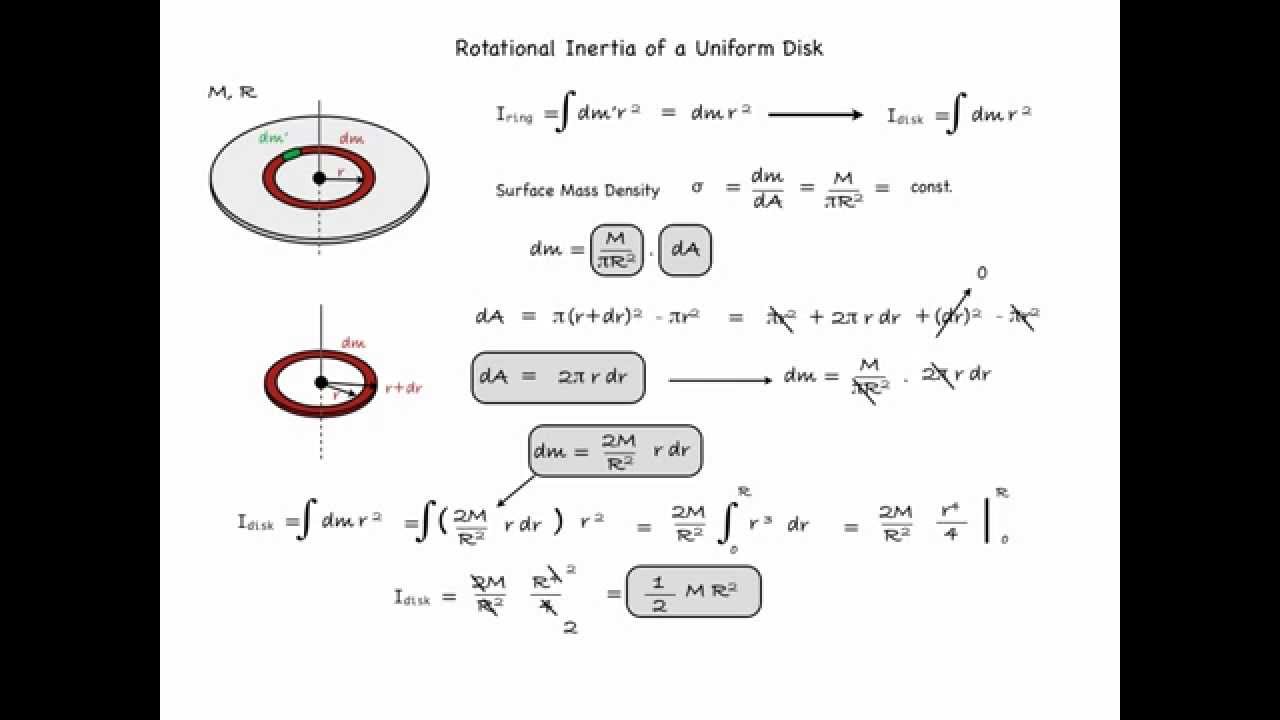
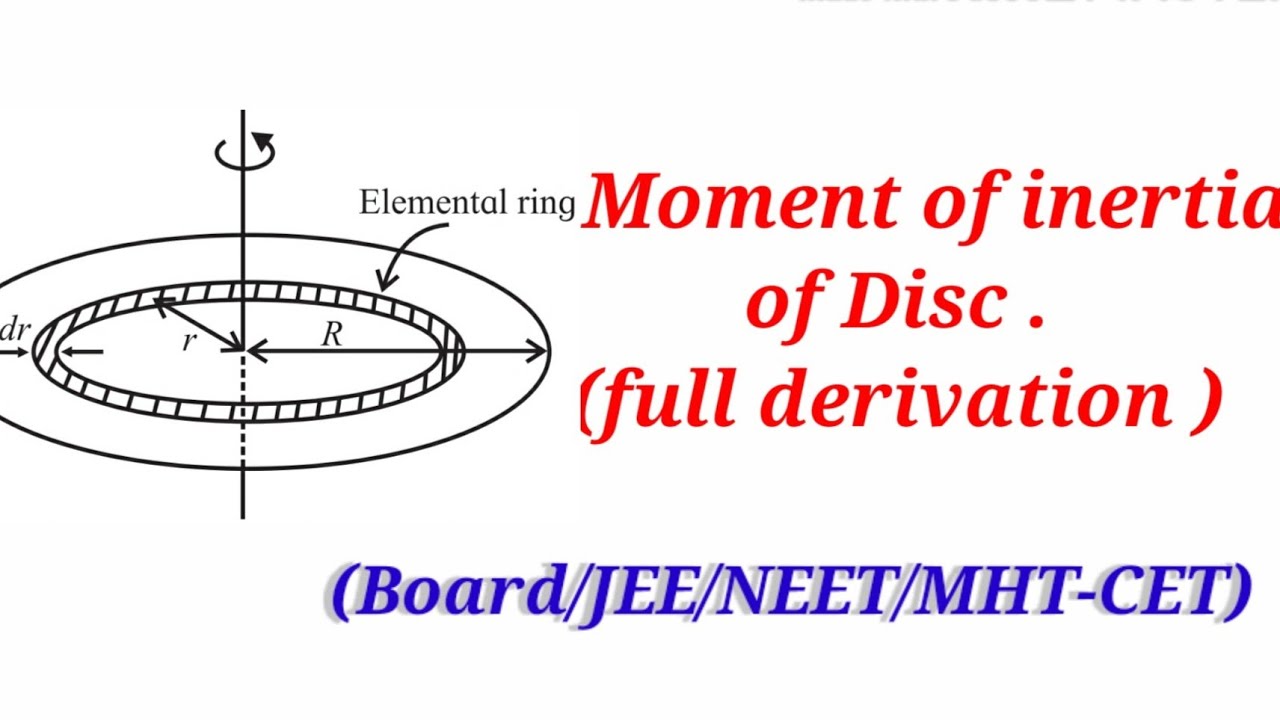
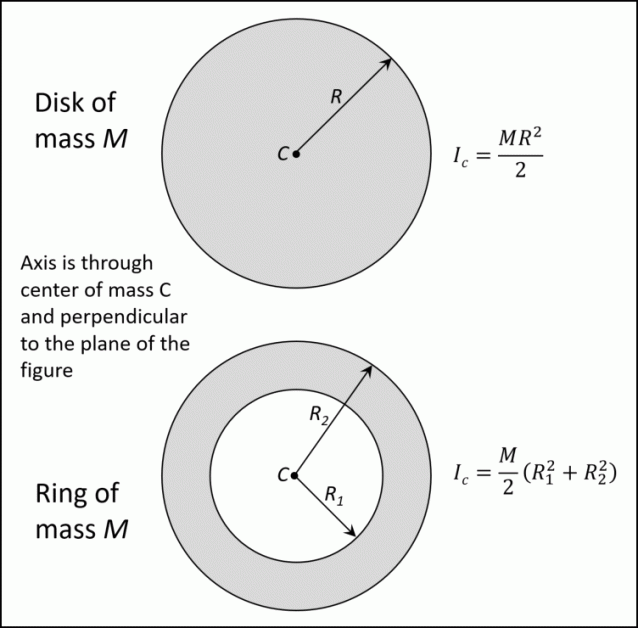
Thus, the rotational inertia of a thin disk about an axis through its CM is the product of one-half the total mass of the disk and the square of its radius. Notice that the thickness of the disk does not effect its rotational inertia. A consequence of this fact is that a cyclinder has the same rotational inertia as a disk, when rotated about an.

Moment of inertia of disk AnswerData
I parallel-axis = 1 2 m d R 2 + m d ( L + R) 2. Adding the moment of inertia of the rod plus the moment of inertia of the disk with a shifted axis of rotation, we find the moment of inertia for the compound object to be. Itotal = 1 3mrL2 + 1 2mdR2 + md(L + R)2. I total = 1 3 m r L 2 + 1 2 m d R 2 + m d ( L + R) 2.

MOMENT OF INERTIA OF A CIRCULAR DISC WITH RESPECT TO IT'S DIAMETER
To develop the precise relationship among force, mass, radius, and angular acceleration, consider what happens if we exert a force F F on a point mass m m that is at a distance r r from a pivot point, as shown in Figure 10.10. Because the force is perpendicular to r r, an acceleration a = F m a = F m is obtained in the direction of F F.

Moment of Inertia of DISC Rotational Motion Class 11 NEET JEE
Rotational inertia is a property of any object which can be rotated. It is a scalar value which tells us how difficult it is to change the rotational velocity of the object around a given rotational axis. Rotational inertia plays a similar role in rotational mechanics to mass in linear mechanics.

How to derive the moment of inertia of a disk YouTube
Theoretically, the rotational inertia, I, of a ring about its center of mass is given by: 2 2 = --M R + R ( 1 2 where M is the mass of the ring, R1 is the inner radius of the ring, and R2 is the outer radius of the ring. See Figure 11.1. The rotational inertia of a disk about its center of mass is given by: I = - 1 -MR2 2

How to derive the formula for the moment of inertia of a disc about an
τ = mr2α. (10.3.3) (10.3.3) τ = m r 2 α. This last equation is the rotational analog of Newton's second law F = ma F = m a, where torque is analogous to force, angular acceleration is analogous to translational acceleration, and mr2 m r 2 is analogous to mass (or inertia). The quantity mr2 m r 2 is called the rotational inertia or moment.
PPT Rotational Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6187632
Moment of Inertia of a Disk. The moment of inertia, which is also denoted by the letter "i", measures the extent to which resistance of an object is rotational acceleration about a particular axis, and is the rotational analog to mass. \ [ML^2\] (mass×length2) is the unit of the dimension of Mass moments of inertia.
NOVA Physics Rotational Inertia of a Uniform Disk YouTube
Moment of inertia, denoted by I, measures the extent to which an object resists rotational acceleration about a particular axis, it is the rotational analogue to mass (which determines an object's resistance to linear acceleration ). The moments of inertia of a mass have units of dimension ML 2 ( [mass] × [length] 2 ).
Rotationl dynamic lecture_12./Moment of inertia of a disc YouTube
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration.

Rotational Mechanics Solved Example 10 Moment of Inertia for Semi
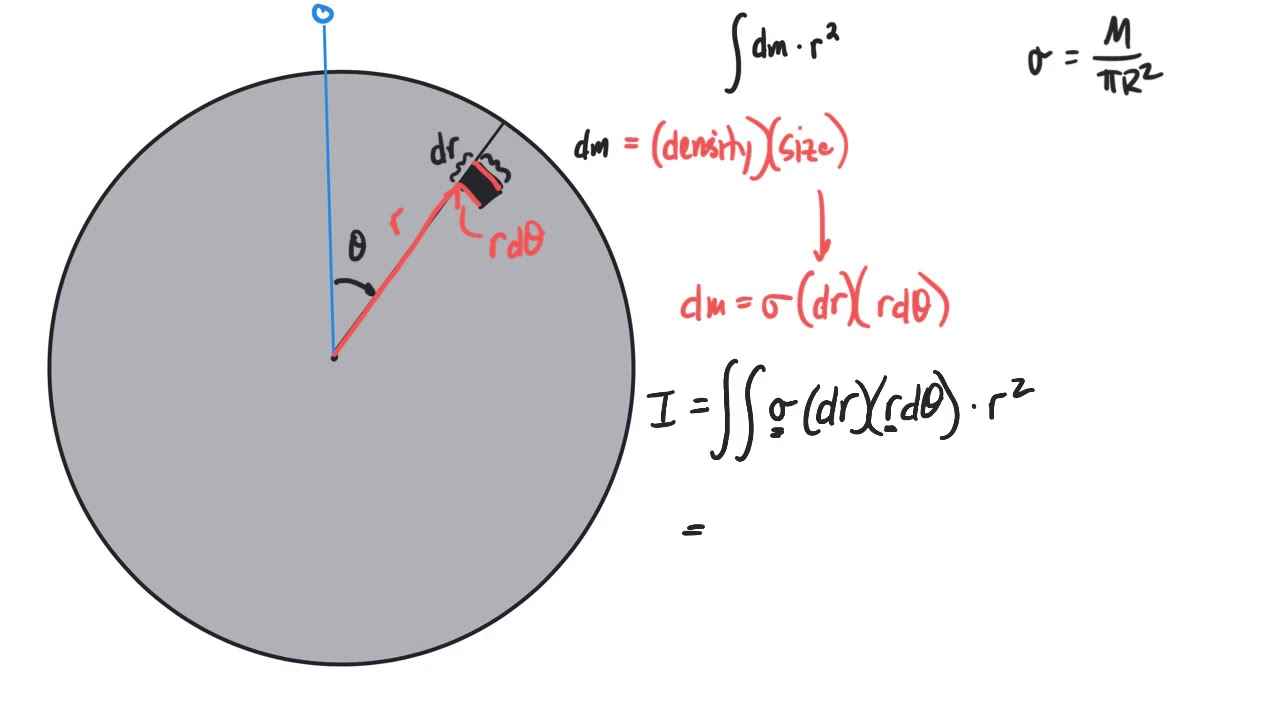
I = ∑ I = ∑ mr2. For an extended body, replace the summation with an integral and the mass with an infinitesimal mass. You add up (integrate) all the moments of inertia contributed by the teeny, tiny masses ( dm) located at whatever distance ( r) from the axis they happen to lie. I =. ⌠.
Moment of Inertia vs. Mass PocketLab
Part of NCSSM Online Physics Collection: This video deals with Rotational Inertia. http://www.dlt.ncssm.eduNCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Caro.