
plate boundary geology Britannica
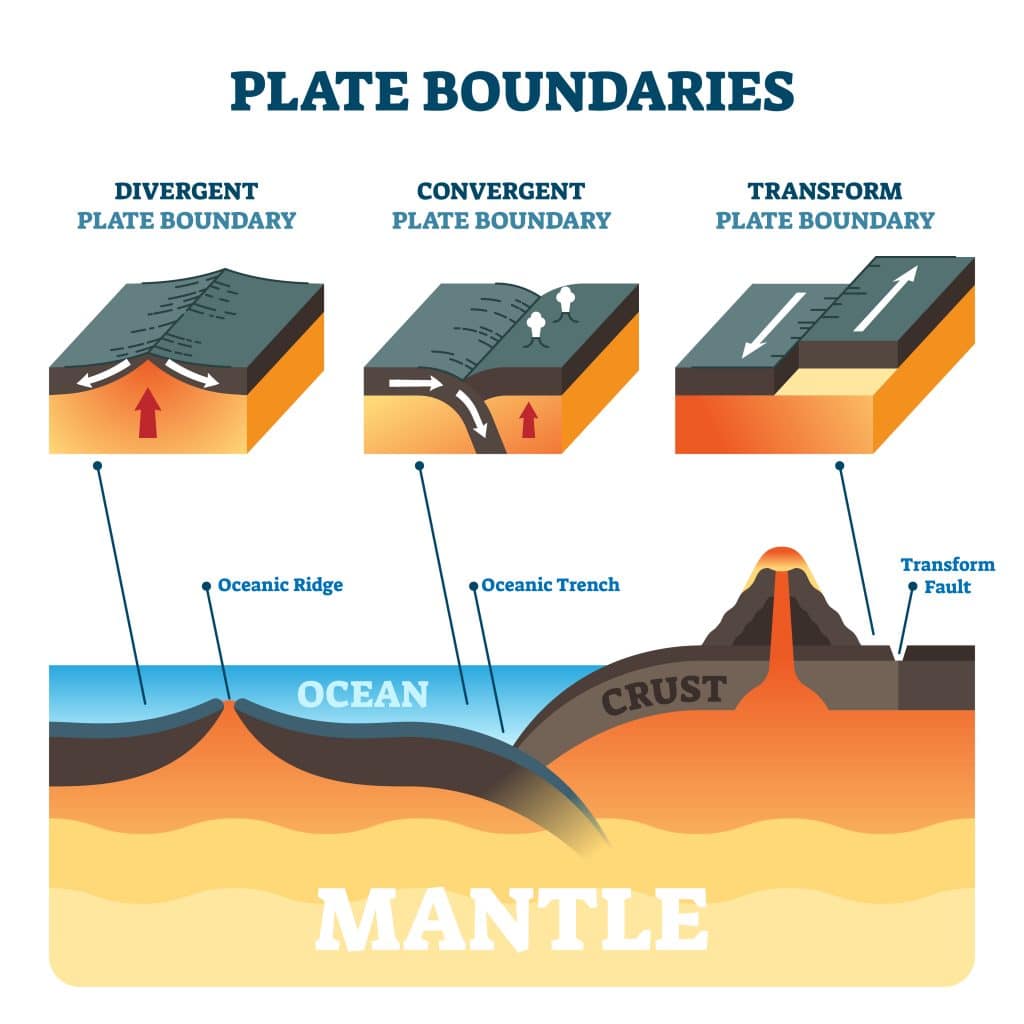
Understanding plate motions [This Dynamic Earth, USGS] Scientists now have a fairly good understanding of how the plates move and how such movements relate to earthquake activity. Most movement occurs along narrow zones between plates where the results of plate-tectonic forces are most evident. There are four types of plate boundaries:
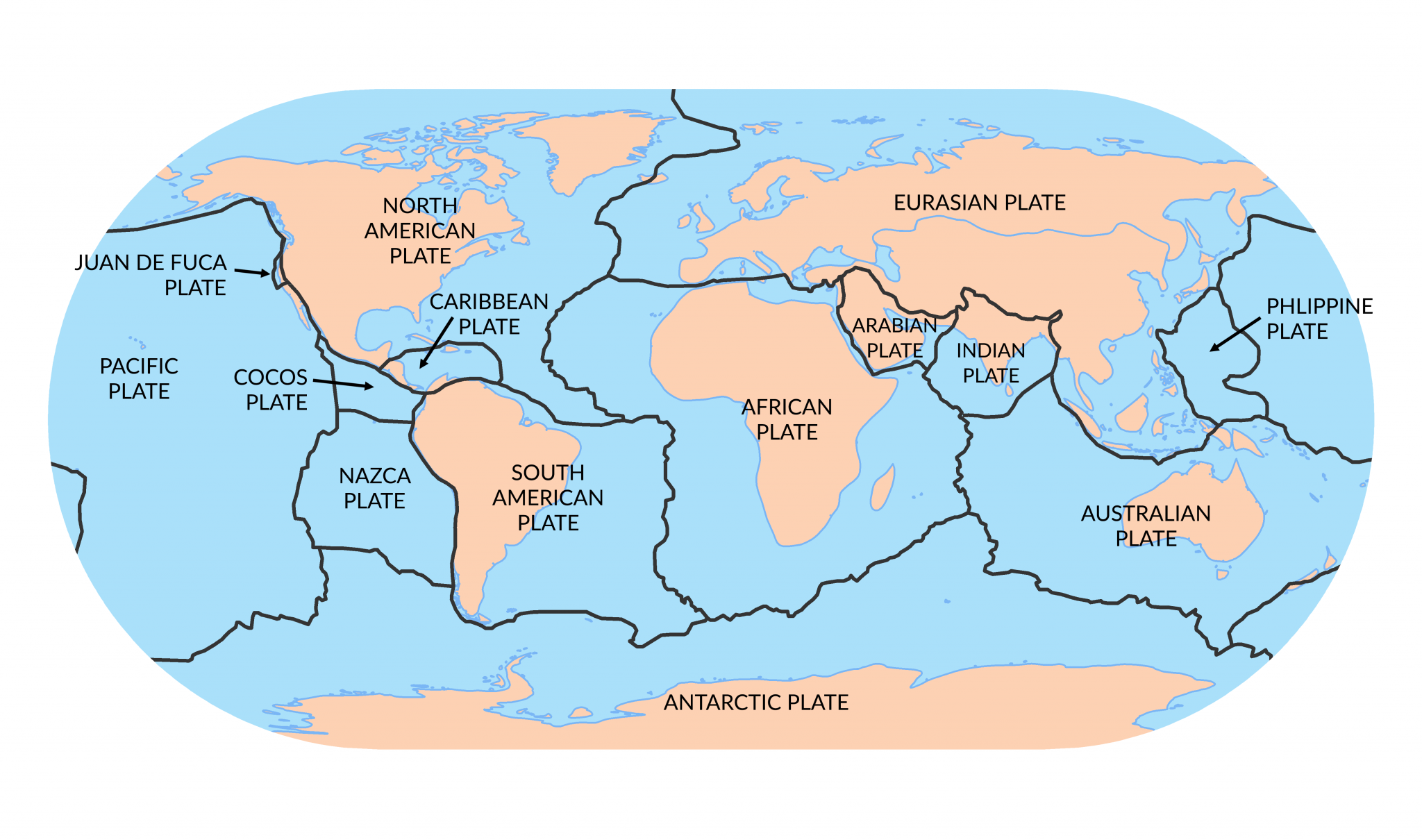
Plate Tectonic Types Divergent, Convergent and Transform Plates
Geology portal Plate tectonics (from Latin tectonicus, from Ancient Greek τεκτονικός (tektonikós) 'pertaining to building') [1] is the scientific theory that Earth 's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. [2]

Tectonic plates movement labeled world map Plate tectonics, Tectonic
. Transform plate boundaries link the other two types of boundaries, for example, "transforming" the motion of a divergent plate boundary into the motion of a convergent boundary. These are.
Theory of Plate Tectonics CK12 Foundation
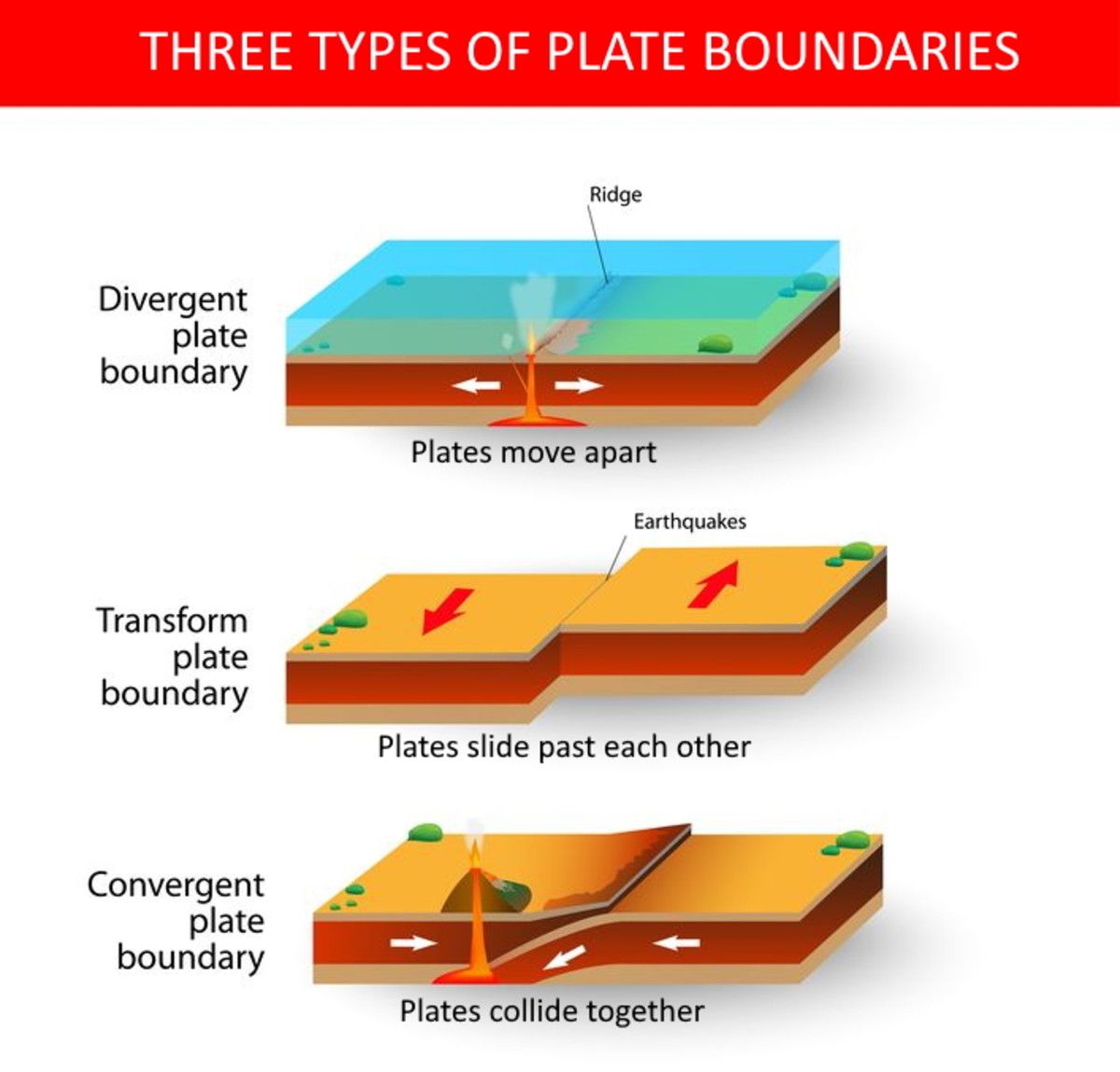
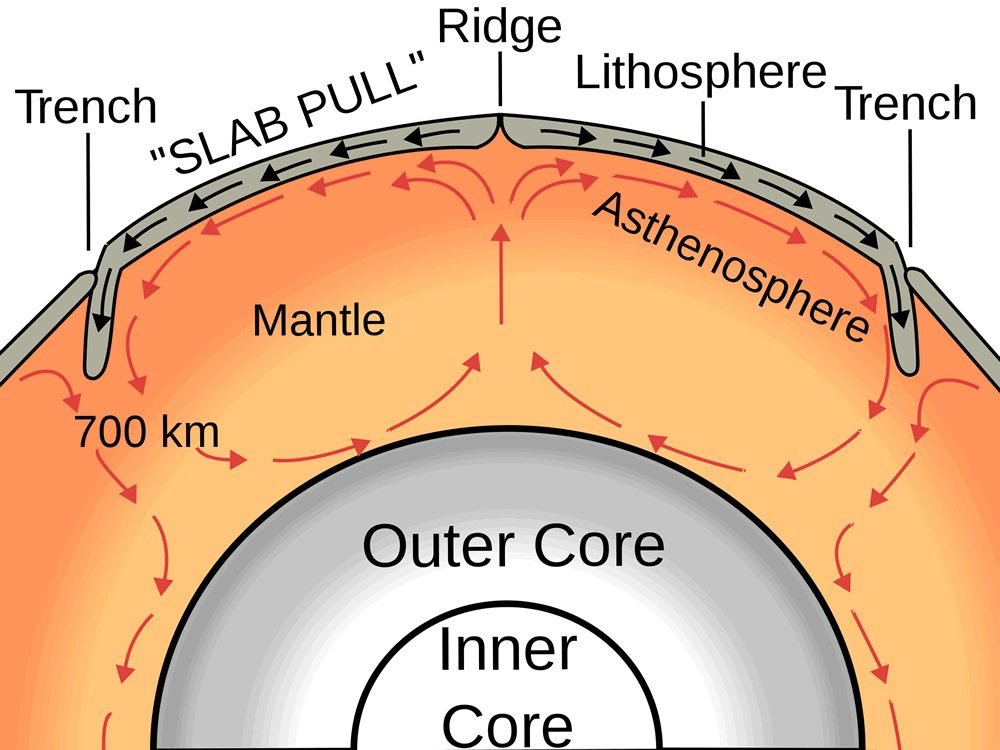
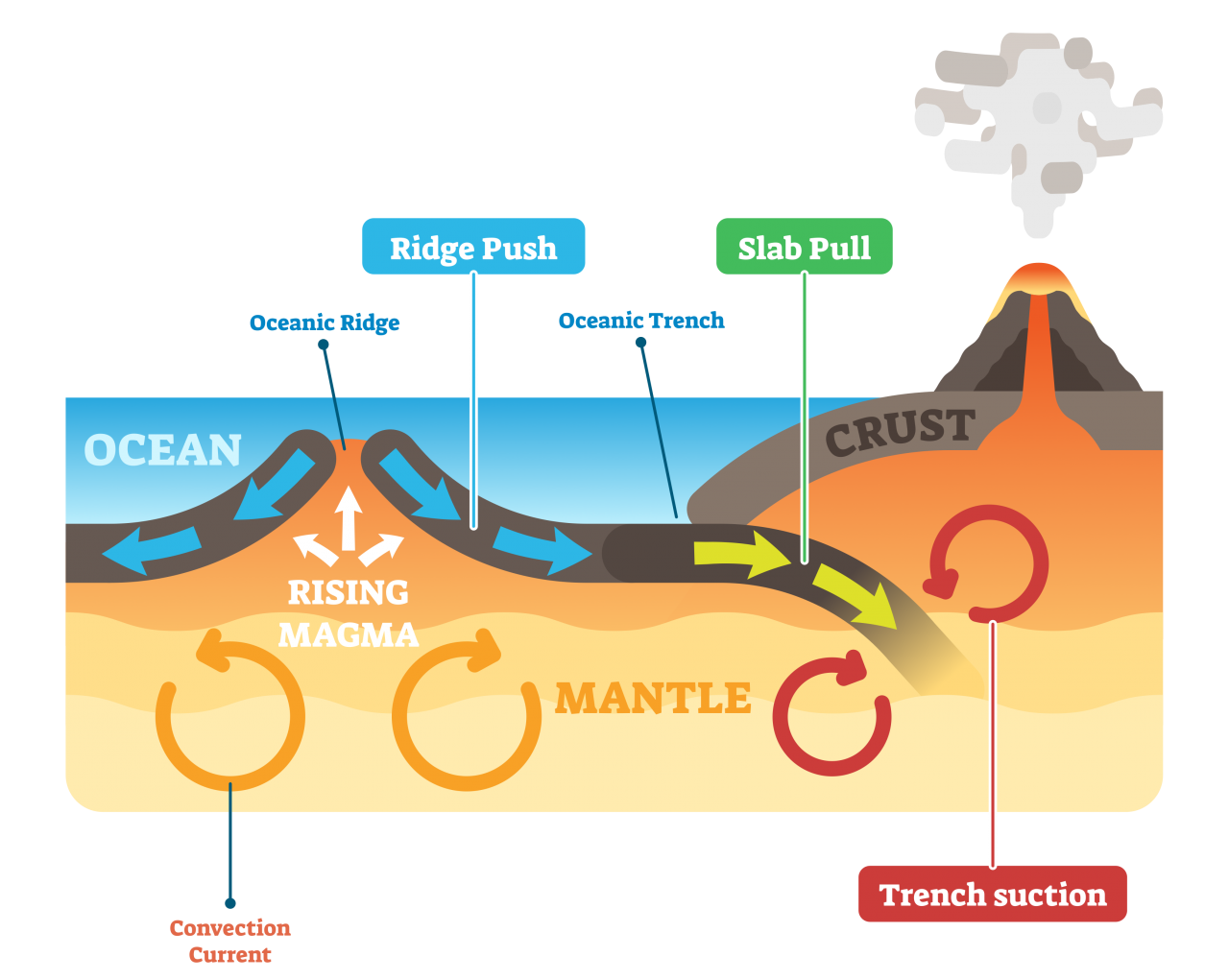
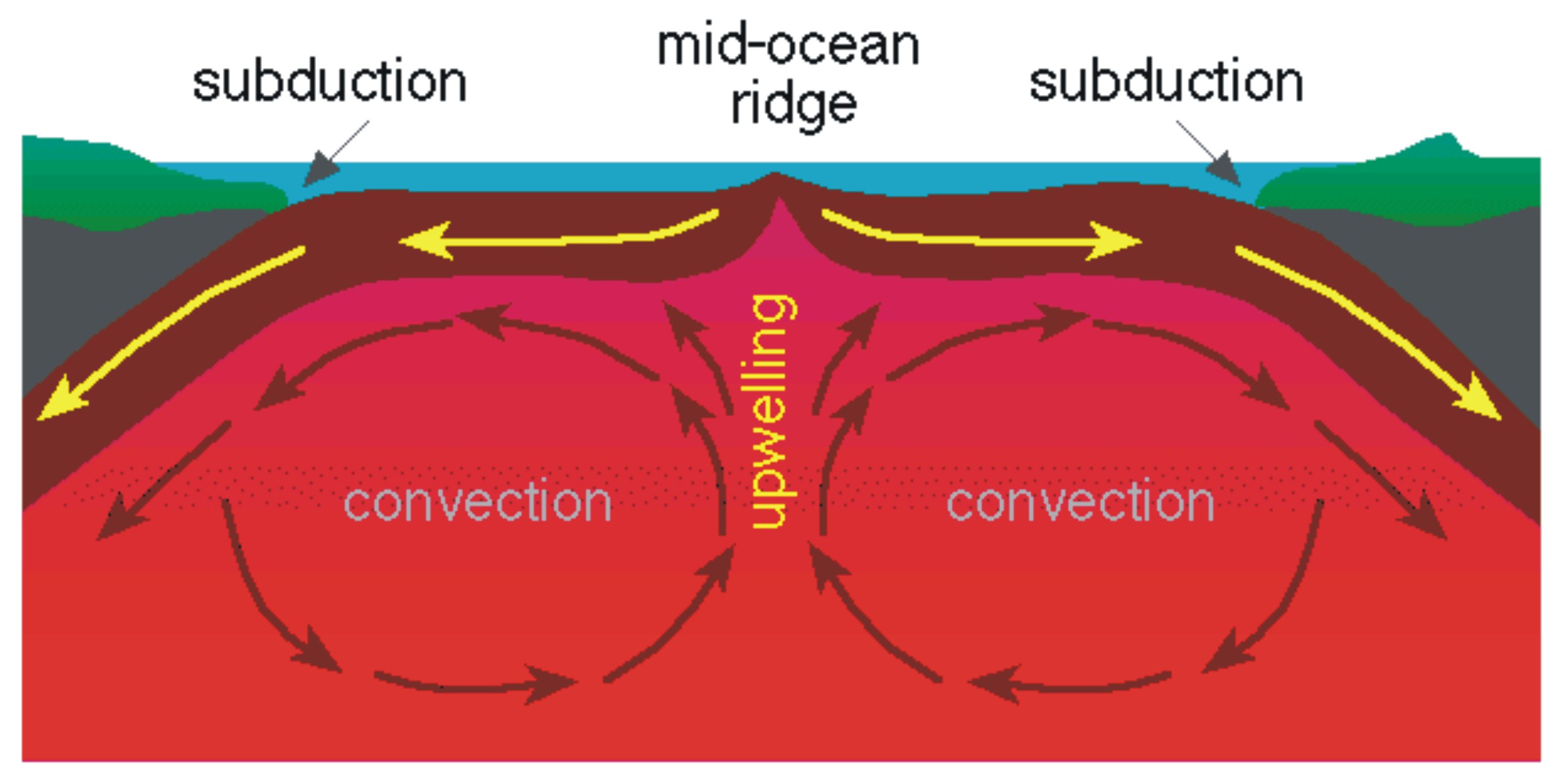
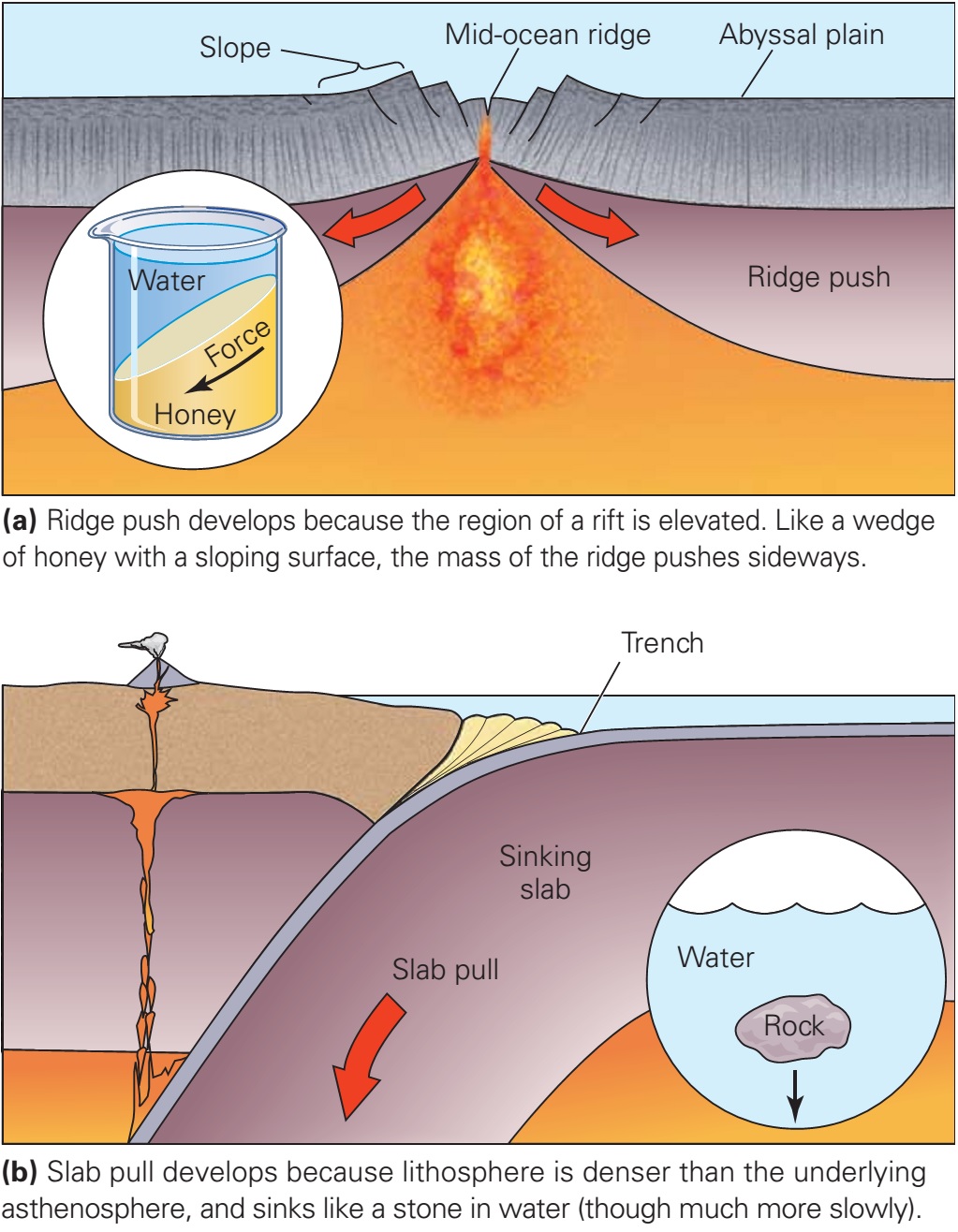
4.1: The Forces Driving Plate Motions. Page ID. Magali Billen. University of California, Davis. The motion of tectonic plates is driven by convection in the mantle. In simple terms, convection is the idea that dense, cold things sink, and buoyant, warm things rise. In the earth the cold sinking things are slabs (subducting plates) and the warm.

2 Schematic representation of the three types of plate boundaries
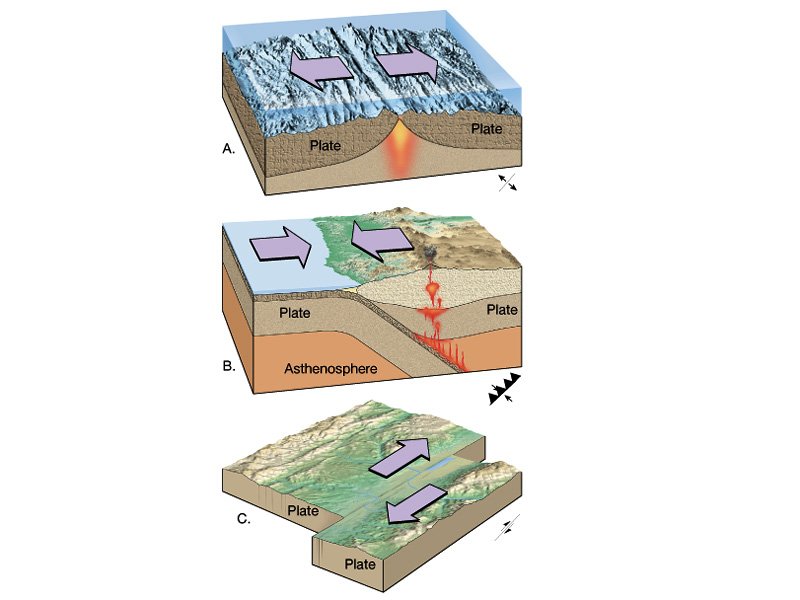
Another kind of plate movement is called a divergent boundary. The di in divergent comes from a Latin prefix meaning apart, so divergent boundaries happen where two tectonic plates move apart. Divergent boundaries can create different kinds of land forms, like rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges. The third kind of plate boundary is called a.
Evolution of the Theory of Plate Tectonics Owlcation
Tectonic plates, the massive slabs of Earth's lithosphere that help define our continents and ocean, are constantly on the move. Plate tectonics is driven by a variety of forces: dynamic movement in the mantle, dense oceanic crust interacting with the ductile asthenosphere, even the rotation of the planet. Geologists studying the Earth use scientific observation and evidence to construct a.
How tectonic plates move? Electrical
The movement of the plates creates three types of tectonic boundaries: convergent, where plates move into one another; divergent, where plates move apart; and transform, where plates move.

Tectonic Plate Movements Plate Tectonics
Key points: Earth's lithosphere, or outermost shell, is broken up into large pieces called tectonic plates. These plates move slowly over the asthenosphere, a layer of softer rock below the lithosphere. On average, tectonic plates move a few centimeters per year. The place where two plates meet is called a plate boundary.
Why do tectonic plates move? Geography
Natural or human-made structures that cross a transform boundary are offset — split into pieces and carried in opposite directions. Rocks that line the boundary are pulverized as the plates grind along, creating a linear fault valley or undersea canyon. Earthquakes are common along these faults.
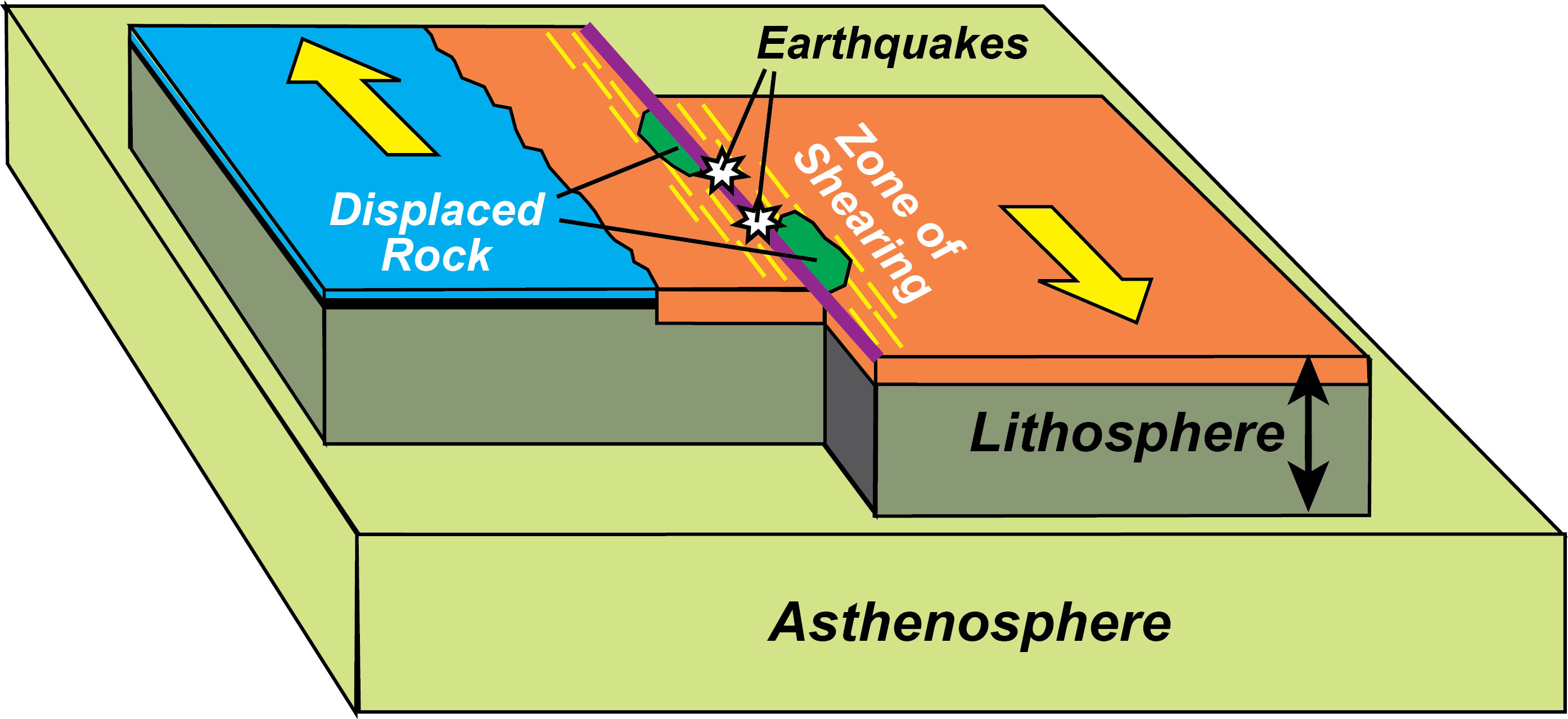
Transform Plate Boundaries Geology (U.S. National Park Service)
Plate boundaries are important because they are often associated with earthquakes and volcanoes. When Earth's tectonic plates grind past one another, enormous amounts of energy can be released in the form of earthquakes. Volcanoes are also often found near plate boundaries because molten rock from deep within Earth—called magma—can travel.
Section 4 The Theory of Plate Tectonics Nitty Gritty Science
Plate tectonics is a theory about how Earth's lithosphere is divided into a series of rigid plates; and, how movements of these plates produce earthquakes, volcanoes, ocean trenches, mountain ranges, and more. Plate Tectonics Animation Watch This Billion-Year Journey of Earth's Tectonic Plates on The New York Times website. Click map above to view.
A Shift to Plate Tectonics The Emergence and Evolution of Plate
Plate boundaries can be located by outlining earthquake epicenters. Plates interact at three types of plate boundaries: divergent, convergent and transform. Most of the Earth's geologic activity takes place at plate boundaries. At a divergent boundary, volcanic activity produces a mid ocean ridge and small earthquakes.

10.4 Plates, Plate Motions, and PlateBoundary Processes Physical Geology
movement. Explain how movement at the three types of plate boundaries causes earthquakes, volcanoes , and mountain building. Identify convergent boundaries, including subduction and collisions, as places where plates come together. Identify divergent boundaries, including rifts and mid-ocean ridges , as places where plates separate. Explain
Tectonic Plates & Plate Boundaries The Dynamic Earth
Plate tectonics refers to the movement of the rigid plates around the surface of Earth. The outer portion of the planet, or lithosphere, is relatively rigid because it is relatively cold. The lithosphere varies in thickness but is typically a hundred or so kilometers thick. It includes the upper mantle and both the continental and oceanic crust.

Plate tectonics Seafloor Spreading, Continental Drift, Subduction
How plate movement operates is being revised all the time as scientists unearth new evidence, however, the detail still remains highly controversial. An online resource from the Geological Society, outlining the chemical and mechanical properties of tectonic plates and how they move.
Learning Geology What Drives Plate Motion, and How Fast Do Plates Move?
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how major landforms are created as a result of Earth's subterranean movements. The theory, which solidified in the 1960s, transformed the earth sciences by explaining many phenomena, including mountain building events, volcanoes, and earthquakes.