Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction Online Biology Notes
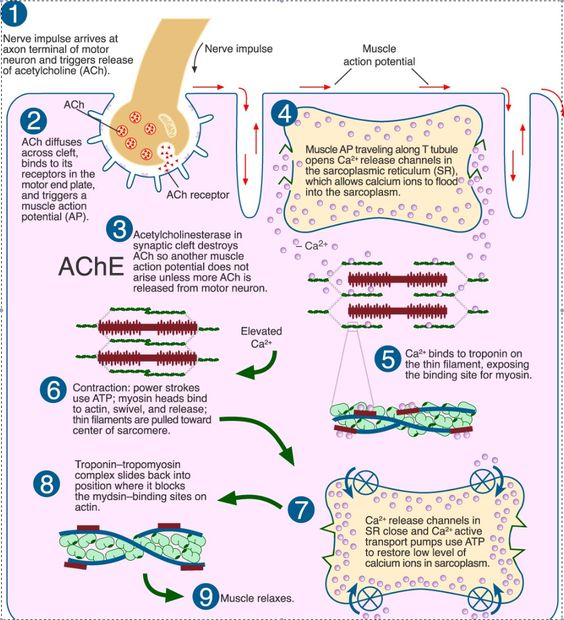
Steps of the Activation of Muscles Neuron action potential at the motor neuron Electrical current flows along a motor neuron Chemical transmission The motor neuron releases Acetylcholine, which crosses the neuromuscular junction to excite the sarcolemma, which is the cell membrane of the muscle fiber. Muscle action potential

Sliding Filament Theory Diagram Quizlet
The Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction | FOUR STEPS HEATHER FIT 1.53K subscribers Subscribe 5.5K 193K views 4 years ago In this video I break down the Sliding Filament.

Sliding Filament Model of Contraction Biology for Majors II
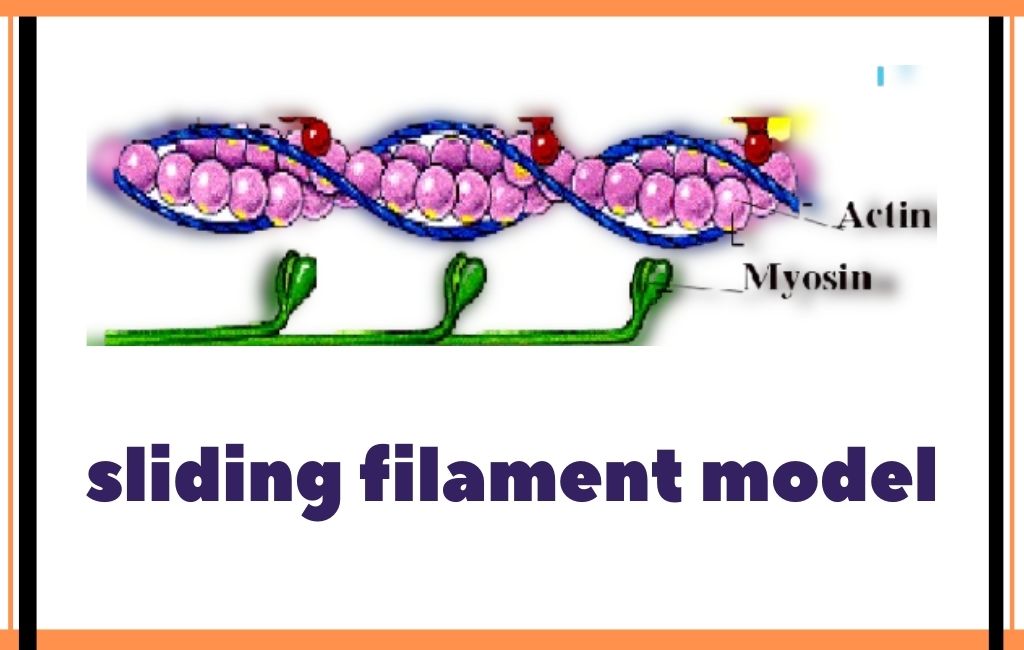
According to the sliding filament theory, the myosin ( thick filaments) of muscle fibers slide past the actin ( thin filaments) during muscle contraction, while the two groups of filaments remain at relatively constant length.

sliding filament theory 6 steps video 4 YouTube
Sliding filament theory explains how muscles contract at a cellular level. Learn more and test yourself with our quizzes here:.more.more Muscle Contraction - Cross Bridge Cycle,.
Explain the sliding filament theory in detail
The sliding filament theory is a suggested mechanism of contraction of striated muscles, actin and myosin filaments to be precise, which overlap each other resulting in the shortening of the muscle fibre length. Actin (thin) filaments combined with myosin (thick filaments) conduct cellular movements.
Sliding Filament Model of Muscle Contraction
The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction was developed to fit the differences observed in the named bands on the sarcomere at different degrees of muscle contraction and relaxation. The mechanism of contraction is the binding of myosin to actin, forming cross-bridges that generate filament movement (Figure 1). Figure 1.
Sliding Filament Theory
The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction is the mechanism by which muscles are thought to contract at a cellular level. It explains the steps in muscle contraction. Advert A good understanding of skeletal muscle structure is useful when learning how sliding filament theory works. What is sliding filament theory?
Of the Following Which Best Describes the Sliding Filament Theory
Sliding Filament Theory: Steps for Muscle Contraction Biology Responding to Change Sliding Filament Theory Sliding Filament Theory The sliding filament theory explains how the muscles contract to generate force, based on the movements of thin filaments (actin) along thick filaments (myosin). Content verified by subject matter experts

Sliding Filament Theory Labster
Sliding filament theory describes the mechanism of muscle contraction. The steps involved are described below (figure 1). Figure 1: Sliding Filament Theory 1: When a nerve signal reaches the muscle cell, calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounding the myofibrils.
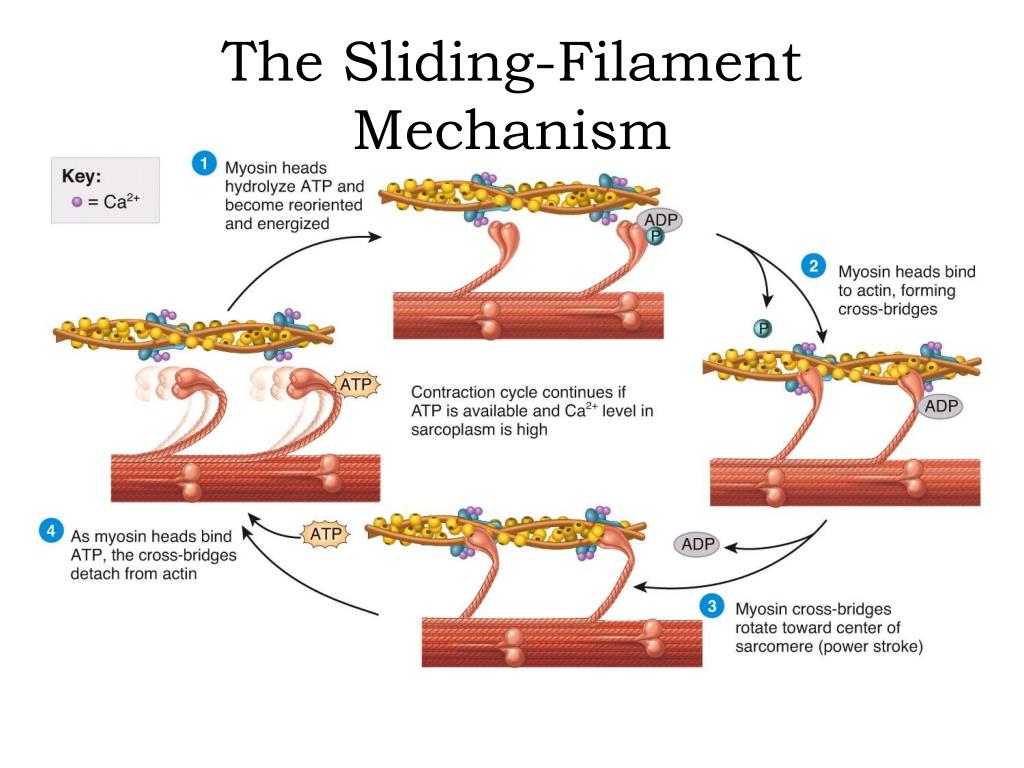
PPT The SlidingFilament Mechanism PowerPoint Presentation, free
The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. Muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers.. The process of contraction starts when an action potential reaches the muscle fiber and triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
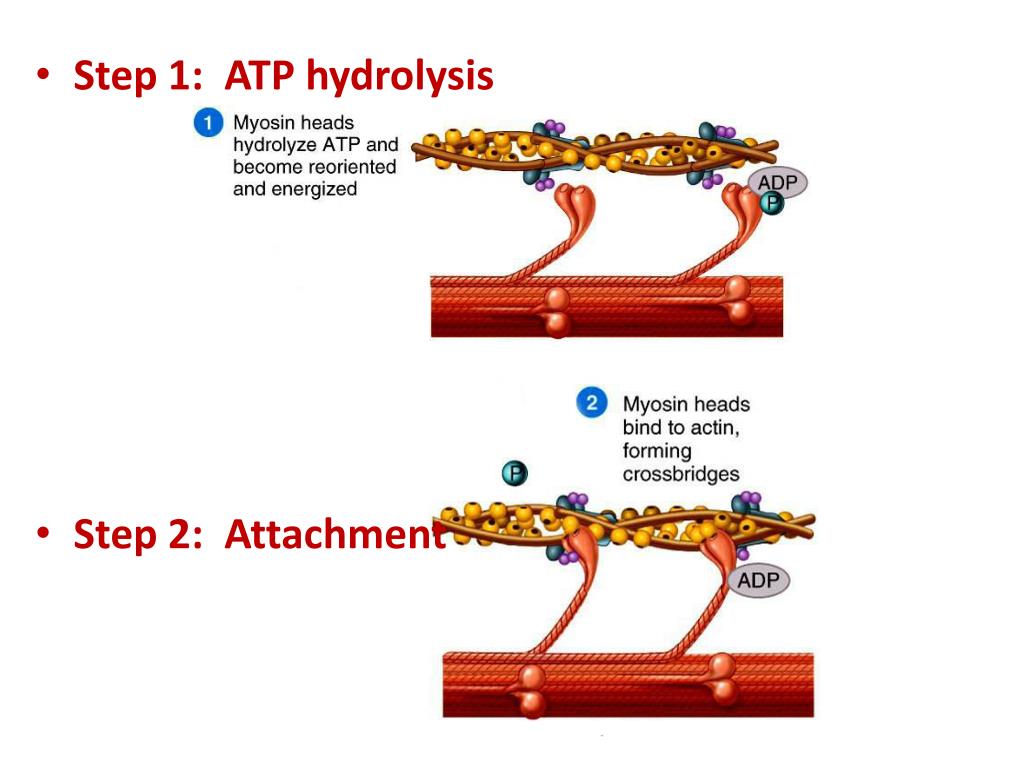
PPT The SlidingFilament Mechanism PowerPoint Presentation, free
Movement often requires the contraction of a skeletal muscle, as can be observed when the bicep muscle in the arm contracts, drawing the forearm up towards the trunk. The sliding filament model describes the process used by muscles to contract. It is a cycle of repetitive events that causes actin and myosin myofilaments to slide over each other.
Diagrammatically explain the sliding filament theory?
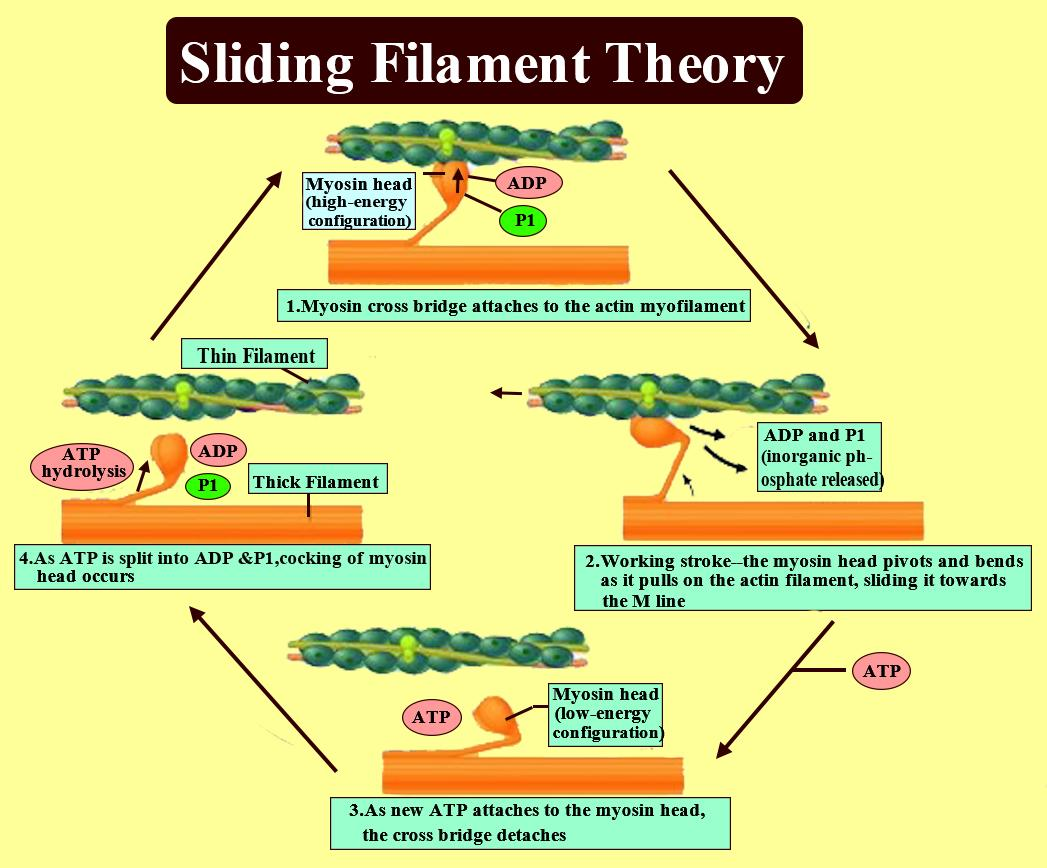
The most widely accepted theory explaining how muscle fibers contract is called the sliding filament theory. According to this theory, myosin filaments use energy from ATP to "walk" along the actin filaments with their cross bridges. This pulls the actin filaments closer together. The movement of the actin filaments also pulls the Z lines.
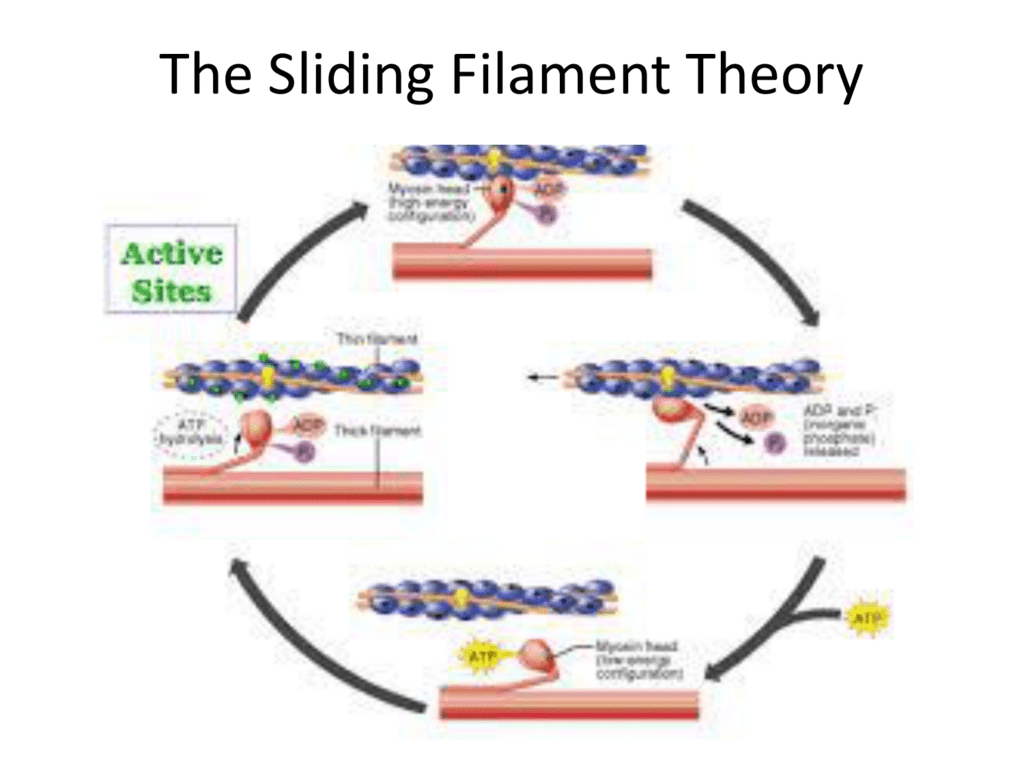
Sliding Filament Theory
Sliding Filament Theory Steps 5.0 (1 review) Sliding filament theory for the contraction of skeletal and cardiac muscle Click the card to flip 👆 (tropomyosin, troponin, myosin binding site, Ca++ channel, Ca++ active transport pumps, ATP, acetylcholine, acetylcholinesterase, Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 11 Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat

2. Structure of the Muscles SimpleMed Learning Medicine, Simplified
Step 1: The brain sends a message (nerve impulse) to the muscle it wants to contract. For example, the brain will send a message to the bicep brachii during a bicep curl. This will cause calcium to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (note: calcium is essential for contraction mechanisms to take place). Step 2:
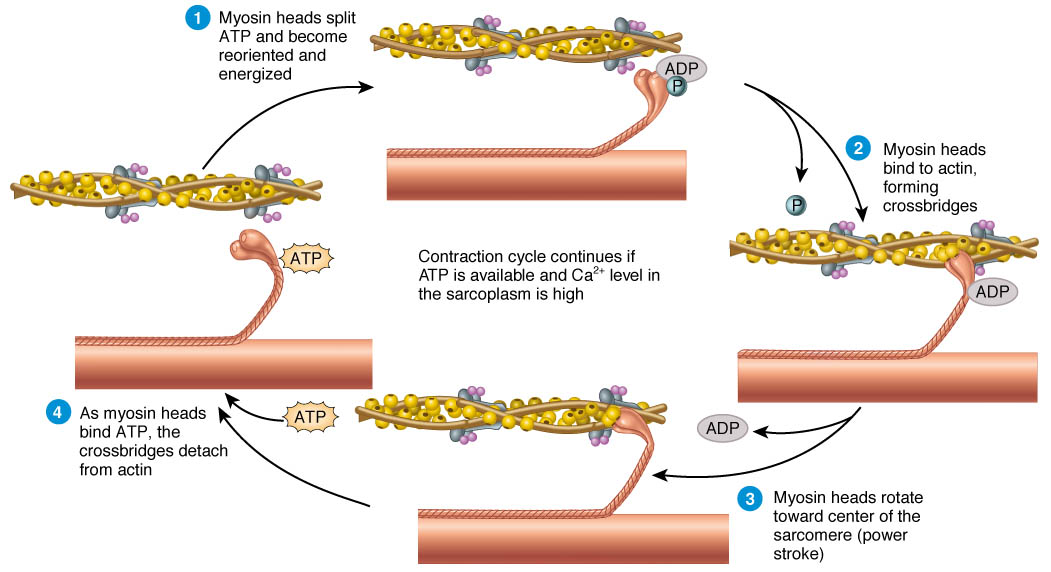
Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction Online Biology Notes
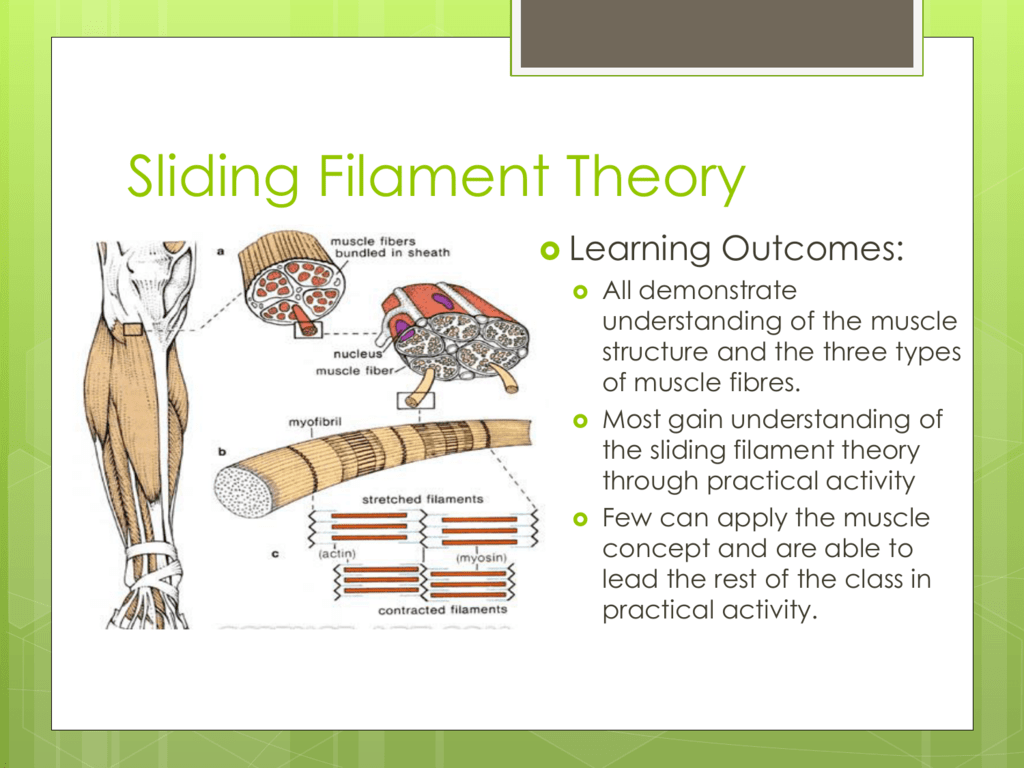
To understand the sliding filament model requires an understanding of sarcomere structure. A sarcomere is defined as the segment between two neighbouring, parallel Z-lines. Z lines are composed of a mixture of actin myofilaments and molecules of the highly elastic protein titin crosslinked by alpha-actinin.
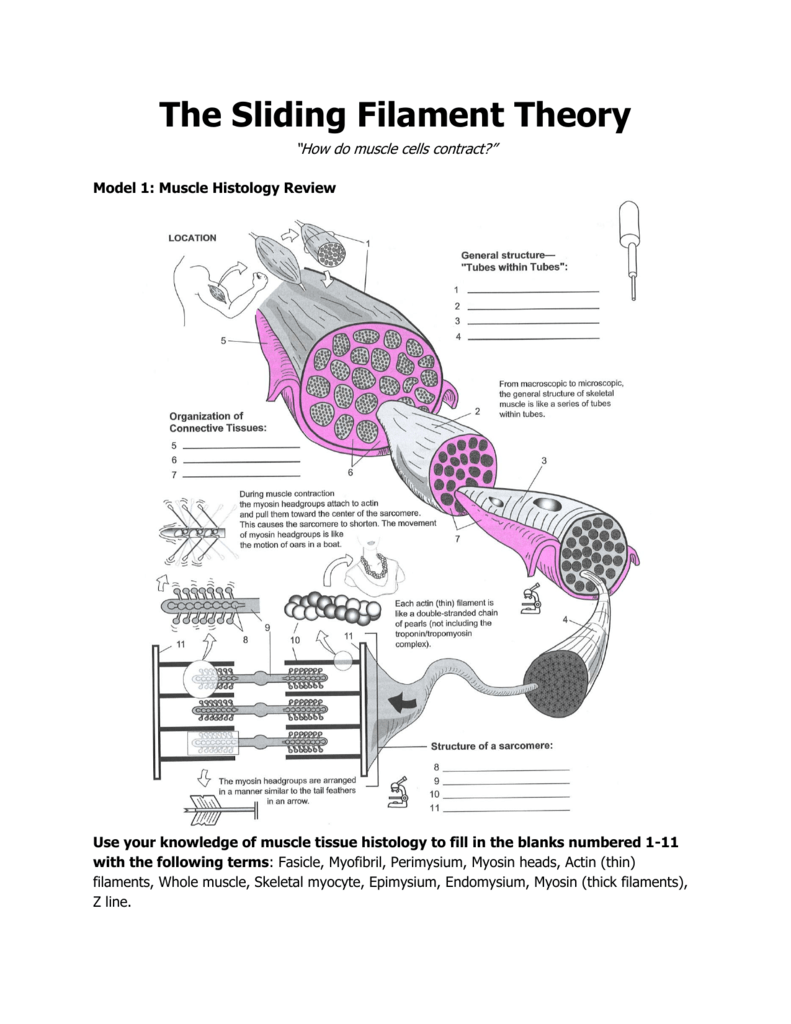
The Sliding Filament Theory
The Sliding Filament Model of Contraction When signaled by a motor neuron, a skeletal muscle fiber contracts as the thin filaments are pulled and then slide past the thick filaments within the fiber's sarcomeres. This process is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction ( Figure 10.10 ).