
Bacterial Conjugation, Transduction, Transformation
Transduction means gene transfer using viral vector carriers If DNA or RNA is introduced into cells by using viral vector carriers, then the technique is called Transduction, and the resulting cells are said to be transduced! It includes virus-based vectors such as lentiviral vectors, adeno-associated viruses (AAV) and adenoviruses.

Difference Between Transformation and Transduction Compare the
The introduction of foreign DNA or RNA into bacteria or eukaryotic cells is a common technique in molecular biology and scientific research. There are multiple ways foreign DNA can be introduced into cells including transformation, transduction, conjugation, and transfection. Transformation, transduction, and conjugation occur in nature as.

Lentiviral production (Step I) and transduction (Step II). Virus
Transfection is the process of deliberately introducing naked or purified nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. [1] [2] It may also refer to other methods and cell types, although other terms are often preferred: "transformation" is typically used to describe non-viral DNA transfer in bacteria and non-animal eukaryotic cells, including plant cells.

Difference Between Transfection and Transduction Definition
Transfection, the process of introducing foreign genetic material into a eukaryotic cell, is an important tool for many cell and molecular biologists, as well as anyone studying the effects of altered gene expression on cellular physiology.

Transfection vs Transduction Key Differences
Transfection is a modern and powerful method used to insert foreign nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. The ability to modify host cells' genetic content enables the broad application of this process in studying normal cellular processes, disease molecular mechanism and gene therapeutic effect.
Frontiers An Overview of Methods and Tools for Transfection of
Transfection is a widely used laboratory cell culture technique that introduces foreign nucleic acids into cells. It is a powerful analytical tool enabling study of gene functions and gene products in cells.

Transfection Vs Transduction Vs Transformation Ppt Powerpoint
Difference between Transfection and Transduction What is Transfection? It is a process of introducing naked DNA or RNA into the eukaryotic cells. Here, the eukaryotic cells involve the opening of pores in their cell membrane (transient pores) through which the uptake of nucleic acid occurs.

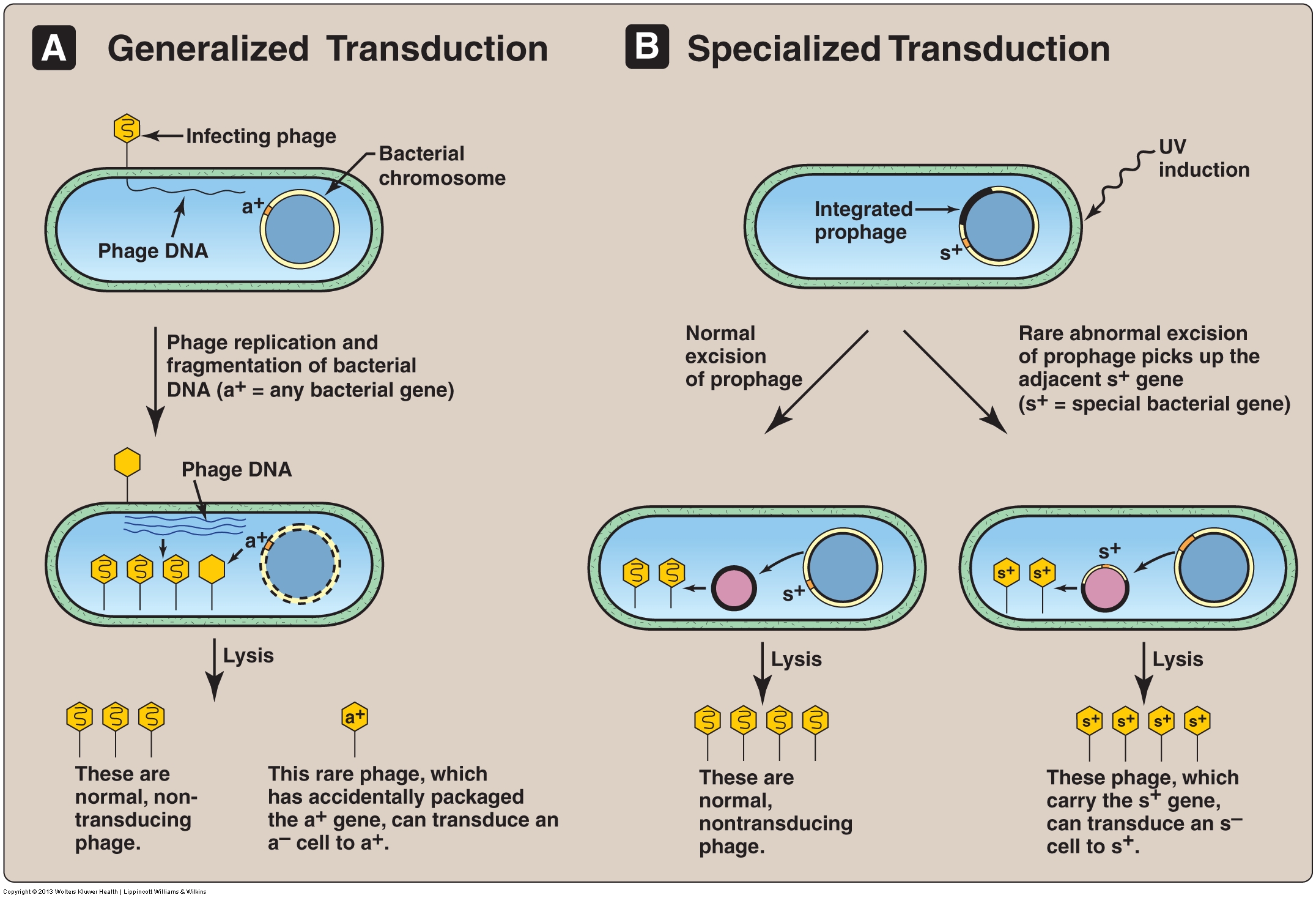
Generalized and specialized transduction processes. Download
"Transfection" refers to the process of introducing foreign DNA or RNA into cells. "Transfected" is the past tense of this verb and is used to describe cells that have undergone this process. Here are some examples of how to use "transfected" in a sentence: The cells were transfected with a plasmid containing the gene of interest.

Difference Between Transfection and Transduction Definition
We compared secreted and whole cell protein levels from HEK293T cells transduced with non-concentrated lentiviral particles (pHR-CMV-TetO 2 _3C-Avi-His6 plasmid) in T25 flask format, with levels from HEK293T cells transiently transfected with equimolar amounts of either the pHLsec or the pHR-CMV-TetO 2 _3C-Avi-His6 plasmids, using anti-His6.

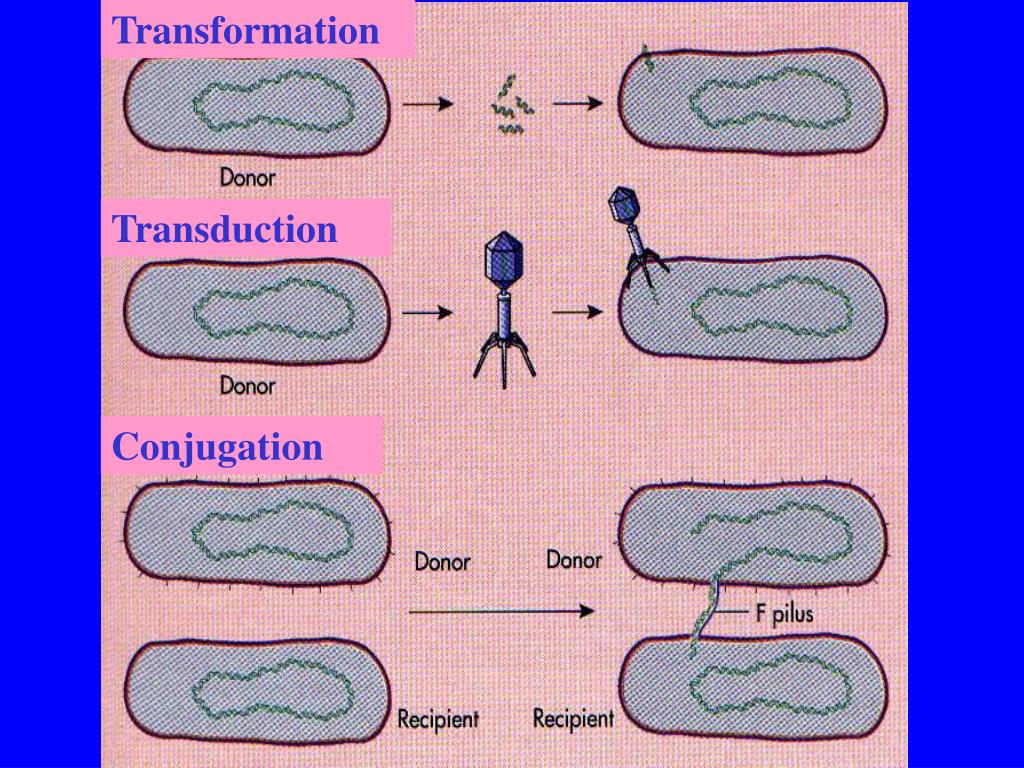
Pathways of horizontal gene transfer. (A) Conjugation is the process of
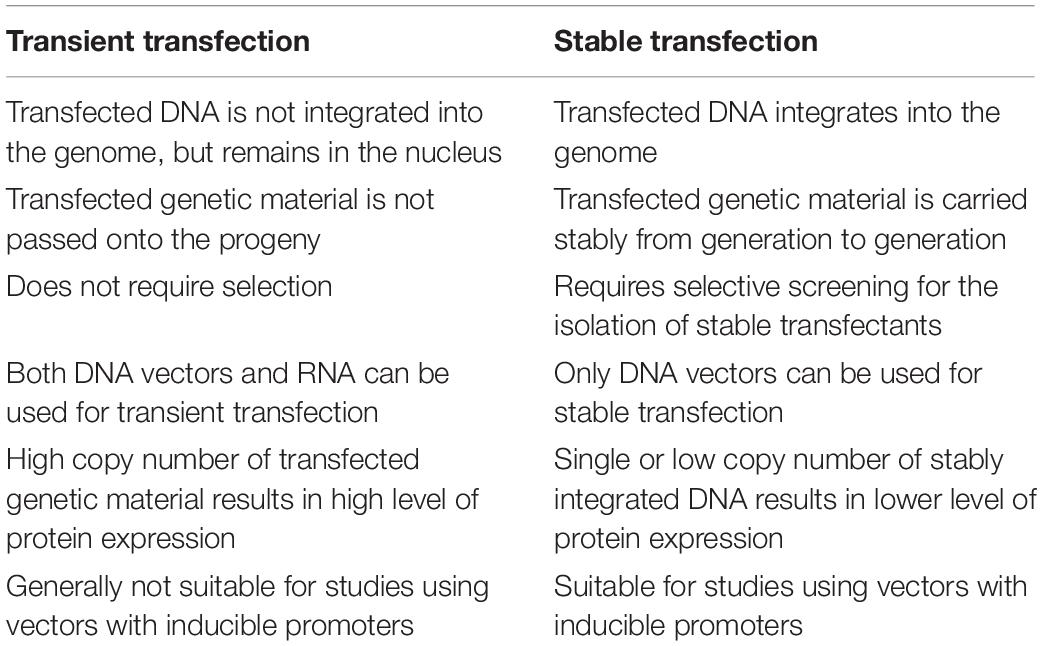
While transfected DNA is translocated into the nucleus for transcription, transfected RNA remains in the cytosol, where it is expressed within minutes after transfection (mRNA) or bound to mRNA to silence the expression of a target gene (siRNA and miRNA) (see Guidelines for RNA Transfection ). Stable transfection

转染和转化之间的区别 新闻 2022 华体会app官网app
Stable transfection. With stable or permanent transfection, the transfected DNA is either integrated into the chromosomal DNA or maintained as an episome. Stable integration of plasmid DNA into the genome is a rare event. Stably transfected cells can be selected by co-transfection of a second plasmid carrying an antibiotic-resistance gene or by.

Bacteria Bacterial transformation, conjugation
Transformation is the uptake of DNA from the environment by a bacterial cell. This phenomenon occurs in nature between bacteria of the same species. Scientists adapted transformation for the propagation of plasmid DNA, protein production, and other applications.
Bacterial
Typically, stable transfection involves the integration of transfected DNA into the host cell genome, allowing transfected cells to pass this DNA to their progeny. Occasionally, stable transfection can occur via the inheritance of nongenomic DNA. Figure 1. Sample stable transfection workflow. In stable transfection, transfected DNA is typically.

Stem Cell Transfection Solutions Mirus Bio LLC
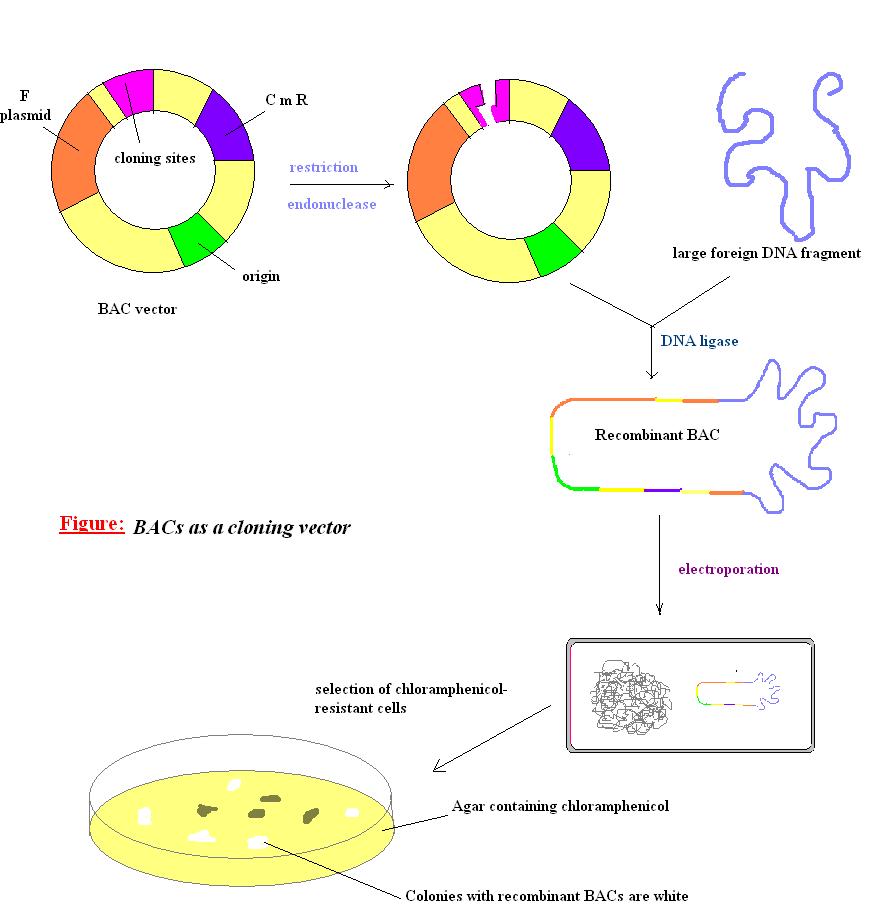
DNA plasmids containing recombinant genes and regulatory elements can be transfected into cells to study gene function and regulation, mutational analysis and biochemical characterization of gene products, and effects of gene expression on the health and life cycle of cells. In addition, plasmid transfection can be used in large-scale.
Difference Between Transfection and Transduction Definition
The main difference between these processes is how they transfer genetic material. During transfection, chemical-based proteins open up the host cell's wall to insert DNA. On the other hand, transduction gets the help of viruses to inject genes into the host cell. [1]
PPT Bacterial PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID709336
Transduction is the process of using a virus to mediate the delivery of DNA fragments or plasmids into a cell, either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. This technique harnesses the natural function of viruses to inject DNA into the infected host, but with a twist. Scientists can modify the viral nucleic acids to contain specific DNA sequences of interest.