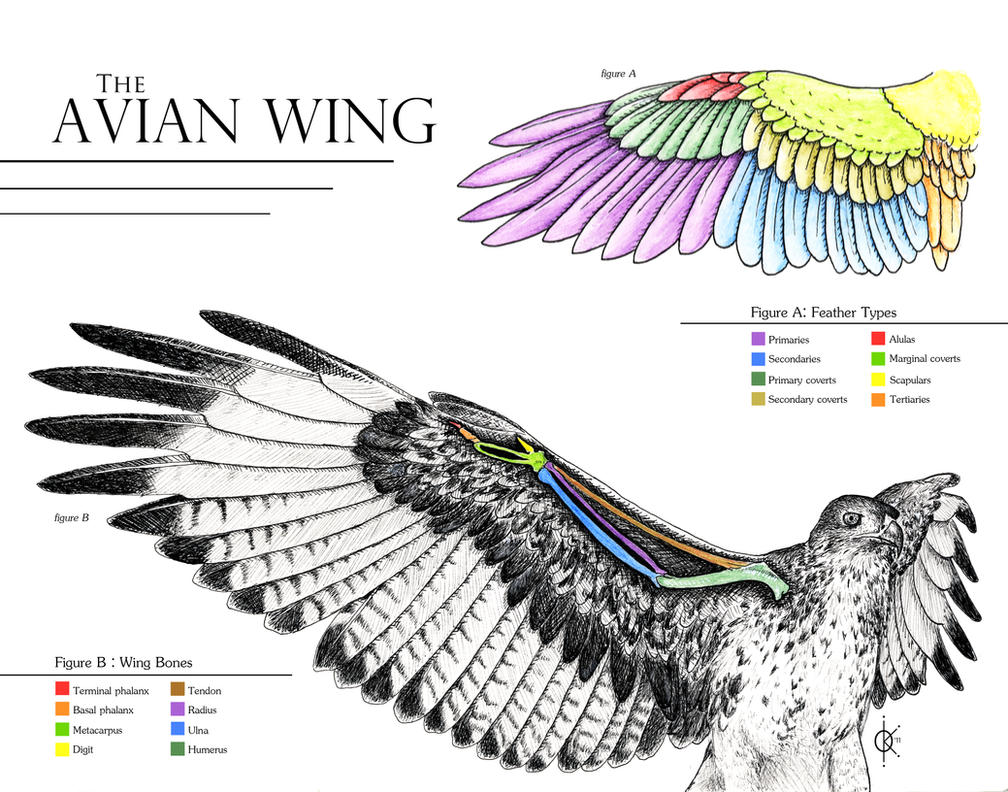
Avian Wing Anatomy by atethirteen on DeviantArt
The wing's aerodynamic characteristics depend on its shape, including its chord distribution, span and aspect ratio, spanwise twist, and other factors, such as if the wing has a winglet. Learning Objectives. Appreciate the physical nature and effects of the trailed wake system behind a wing of finite span.
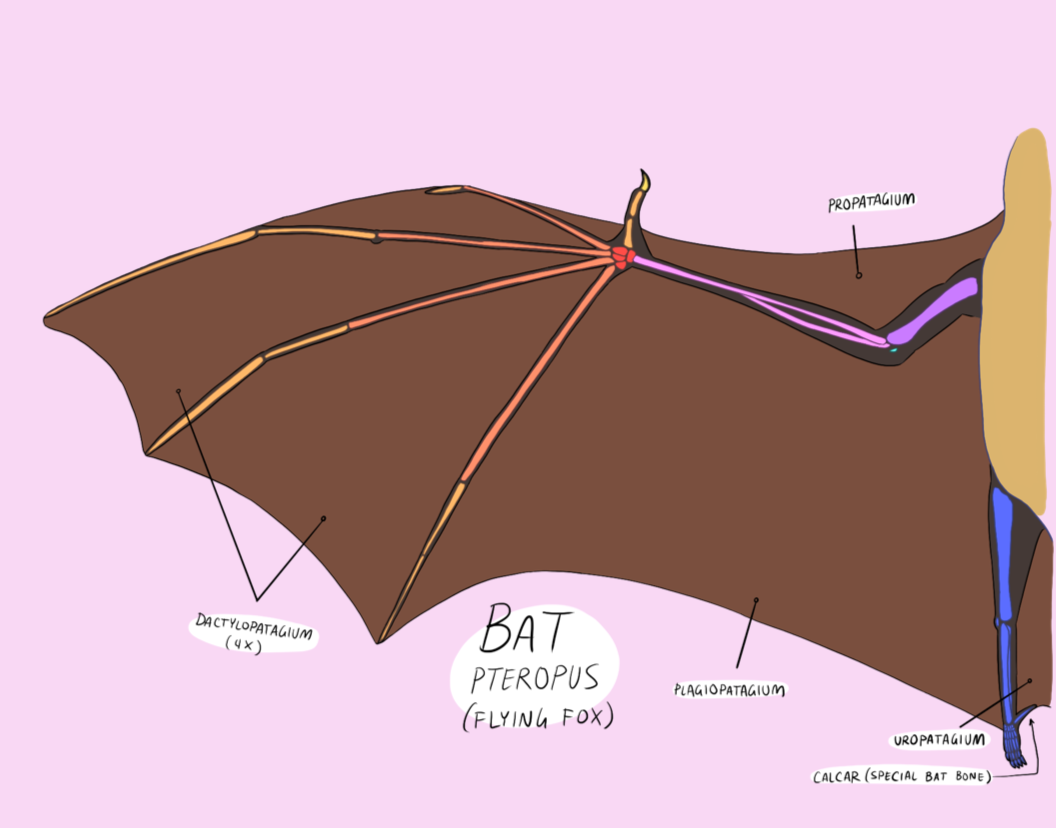
Wing Anatomy
I am trying to create a MATLAB script to plot the Bending Moment Diagram (BMD) and Shear Force Diagram (SFD) as a function of spanwise distance, x, along a wing from the wing root (x=0) to the wingtip (x=b/2). I will be considering the case where the lift generated by the wing is 2.5 times the weight of the wing (so n=2.5).
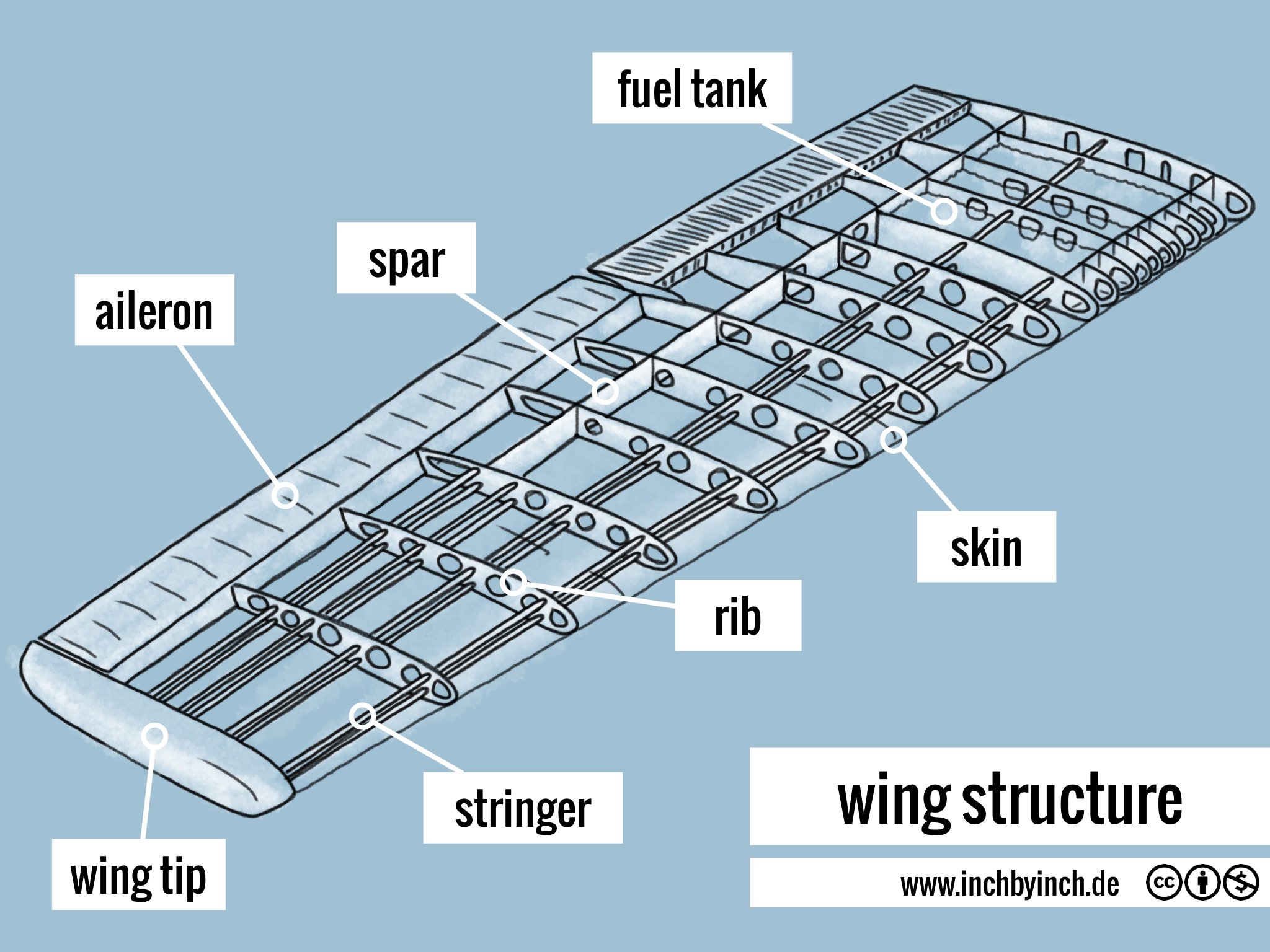
INCH Technical English wing structure
During flight, airflow over the wing of an aircraft will generate two of the four main aerodynamic forces. To get started, we need a simple free body diagram showing the forces acting on an airfoil. In the diagram below, two of the main aerodynamic forces are shown acting on an airfoil. Lift and drag are directly related to the attack angle.

Basic structure of an aircraft wing Download Scientific Diagram
The wing chord is the distance from its leading edge to its trailing edge in the streamwise direction, i.e., parallel to the airplane's longitudinal axis. The chord is given the symbol . On many airplanes, the chord changes along the wing's span, i.e., as in the above figure, mainly for aerodynamic reasons.

Image result for bird wing anatomy Wing anatomy, Wings drawing
A positively cambered airfoil with a zero lift angle of attack of -1.2 degrees. The relevant equation for the lift coefficient is. The lift-curve slope is given as 6.1 per radian angle of attack. Notice that 360 radians so 1 radians, i.e., = 6.1 per radian is equal to 0.1065 per degree.
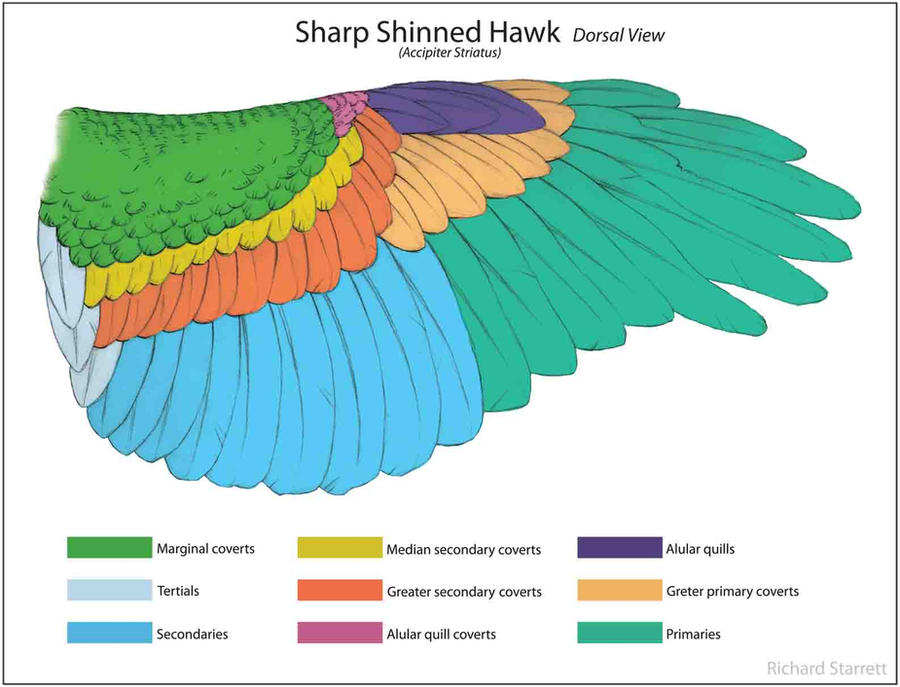
Wing Diagram by Kruggar on DeviantArt
Interactive Simulations. Over twenty years ago, NASA Glenn Research Center developed this collection of interactive simulation exercises to accompany our Beginners Guide to Aeronautics educational content. Students and others in academia, industry, and those with an interest in aeronautics, visit these pages daily to learn and refresh their.

Wing Anatomy Wing anatomy, Wings drawing, Wings art
Both the upper and lower surfaces of the wing act to deflect the air. The amount of lift depends on the speed of the air around the wing and the density of the air. To produce more lift, the object must speed up and/or increase the angle of attack of the wing (by pushing the aircraft's tail downwards). Speeding up means the wings force more.

Pin by Marina Rabiruchi on DOLL INSP N REF Bird drawings, Bird
4.4.2: Structural elements and functions of the wing. Providing lift is the main function of the wing of an aircraft. A wing consists of two essential parts. The internal wing structure, consisting of spars, ribs, and stringers, and the external wing, which is the skin. Ribs give the shape to the wing section, support the skin (prevent buckling.
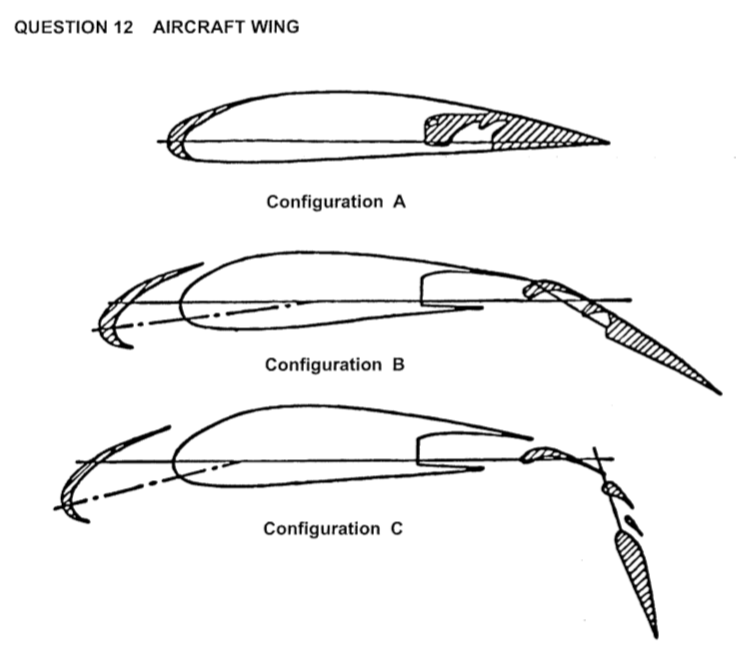
the attached diagram shows an aircraft wing in
A fixed wing distinguishes an airplane from a flywheel (ornithopter) and a helicopter, and the presence of an engine - from the glider. The difference of an airplane from the airship and aerostat is that the airplane uses an aerodynamic method of creating lift , - not the aerostatic. So, the Wing is intended to create the Lift necessary for.
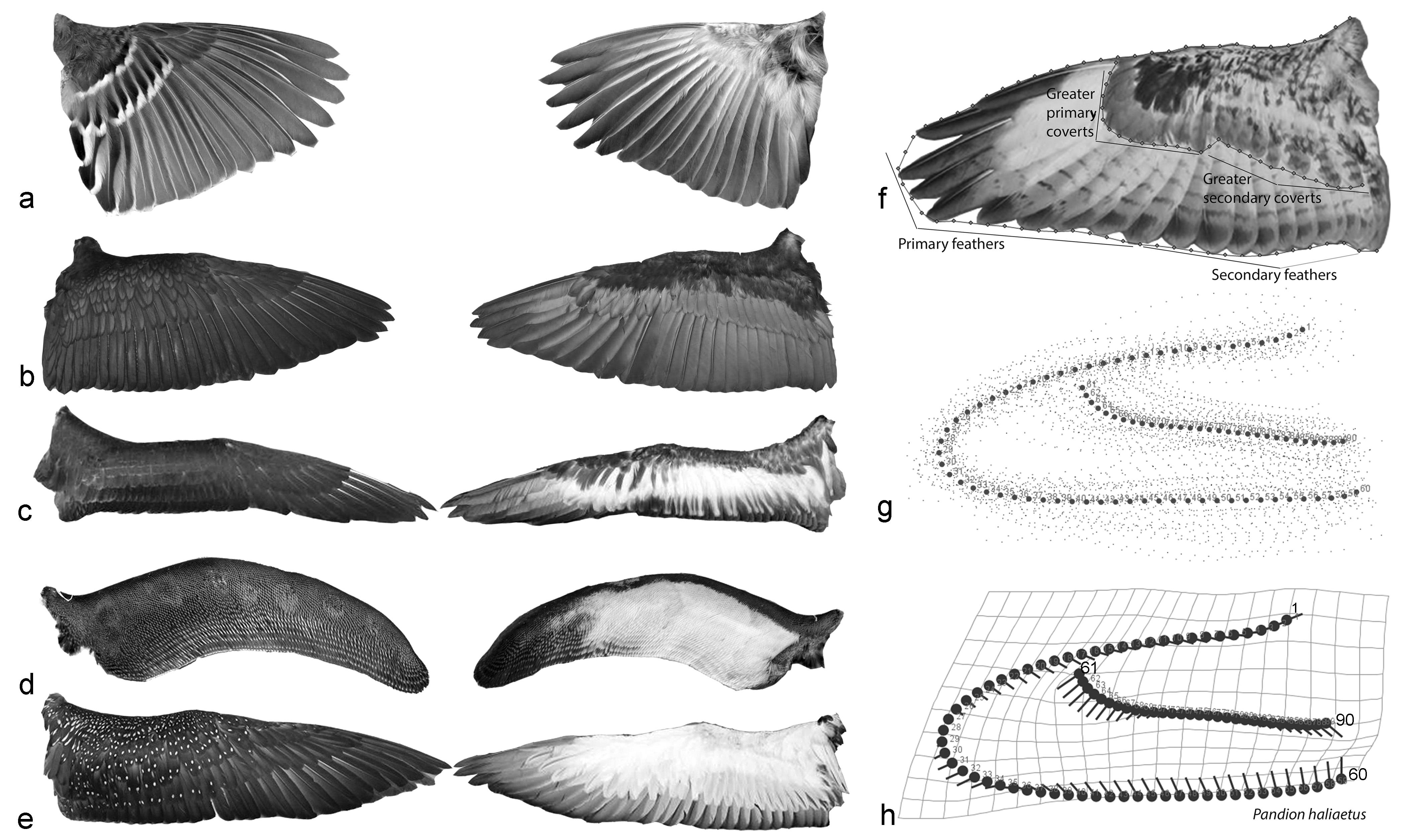
Shape of Bird Wings Depends on Ancestors More Than Flight Style
Lift distribution, Shear diagram and Bending Moment Diagram of a typical wing Wing Structural Components. The primary objective of the wing's internal structure is to withstand the shear and bending moments acting on the wing at the Ultimate load factor. The secondary objective is to make the wing as light as possible without compromising the.

Pin on Drawing file
The wing skins is a semi-monocoque structure are load bearing and carry and transmit shear loads into the neighbouring spar caps and stiffeners. This concludes this post on the wing structural layout. The next post provides a more detailed look at the design and operation of a typical high-lift system.
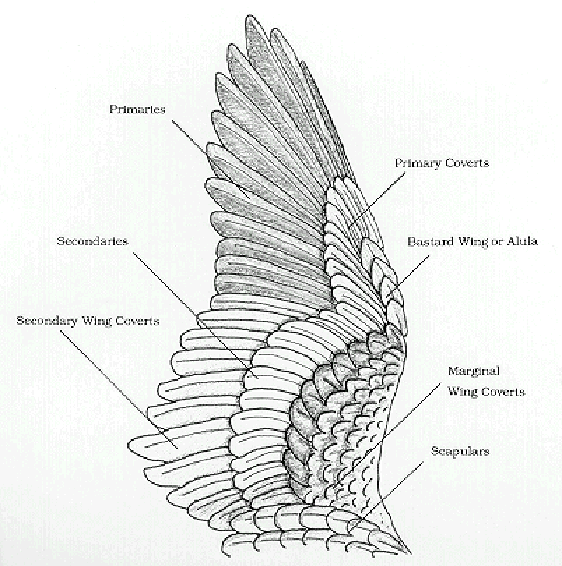
Birds Of A Feather Update Wing Anatomy and Joints
On this page: Weight. Lift. Drag. Thrust. A force may be thought of as a push or pull in a specific direction. A force is a vector quantity so a force has both a magnitude and a direction. When describing forces, we have to specify both the magnitude and the direction. This slide shows the forces that act on an airplane in flight.

AirplaneWingPartDiagramTerminology.png 1,023×649 pixels Aerospace
Give. Lift is the vertical (up and down) force acting on a wing. The focal point of this lift force is called the center of pressure. In flight, as the wing changes its angle to the oncoming flow of air, the center of pressure moves back and forth along the surface of the wing. When the center of pressure and the center of gravity coincide, the.
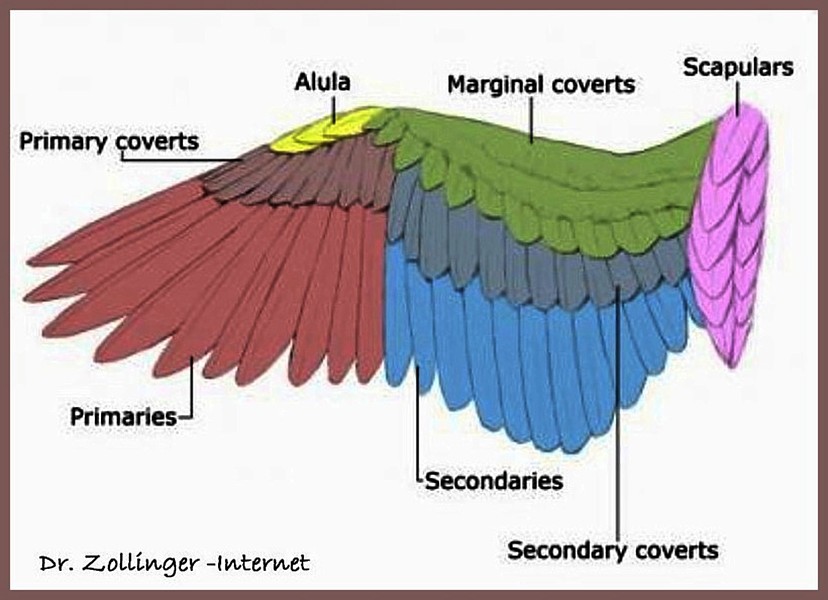
Swan Lovers
Aircraft wings are a feat of modern engineering. Without them, flight simply couldn't take place. There are actually many parts to a wing. Different aircraft have different shapes and styles of the wing, but the general principle is the same. Today we will talk you through parts of a wing and give a detailed explanation of some technical terms too!

Pin on _Drawing Animals and Beasts
Wings. Vertical and Horizontal Stabilizer. Flaps and Spoilers. Fuselage. NASA-Glenn-Airplane-Parts. This page shows the parts of an airplane and their functions. Airplanes are transportation devices which are designed to move people and cargo from one place to another. Airplanes come in many different shapes and sizes depending on the mission.
Airplane Wing Diagram ClipArt ETC
The wing area is a projected area and is almost half of the total surface area. The aspect ratio (AR) of a wing is defined to be the square of the span (s) divided by the wing area (A) . Aspect ratio is a measure of how long and slender a wing is from tip to tip. For a rectangular wing, this reduces to the ratio of the span to the chord length (c):