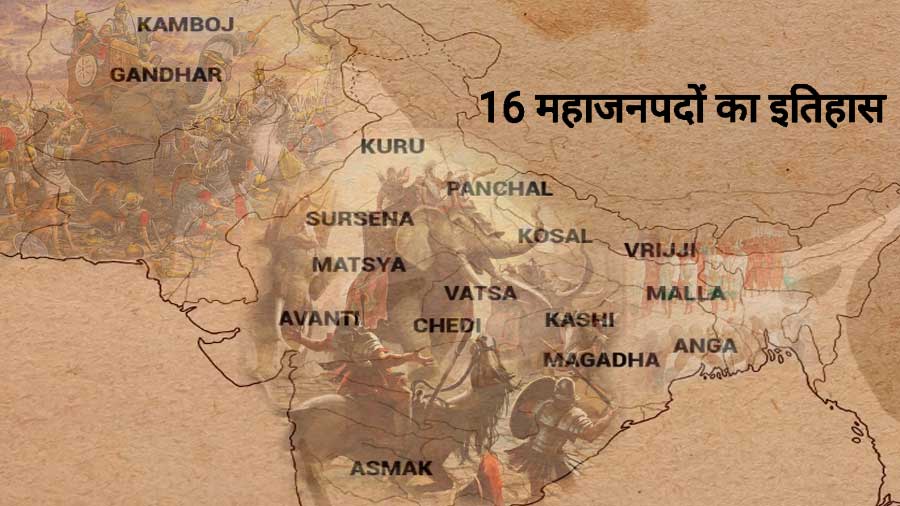
16 Mahajanapadas of Ancient India History, Location and Capitals SamanyaGyan
India Subcontinent Back to 600 BC - 200 BC West Asia Map . Various kingdoms existed in the Indian Subcontinent since ancient times. Yet not until 321 BC did the Maurya Empire unite much of India. This civilization lasted until 185 BC, where it fell to other civilizations in the Subcontinent, such as the Sunga Empire, who retained most of the.

Magadha empire ( ancient Indian history ) ! 600 BC ! Ssc Upsc Railway’s exams YouTube
The changing map of India from 1 AD to the 20th century. Battles were fought, territories were drawn and re-drawn. An amateur historian has caught these shifts in a series of maps. India's.

India Historical Maps
The Vatsa state emerged from Kaushambi. The Cedi state (in Bundelkhand) lay on a major route to the Deccan. South of the Vindhyas, on the Godavari River, Ashvaka continued to thrive. The mid-Ganges valley was dominated by Kashi and Koshala.

Chapter 8 PostGupta Period I (600AD 750AD) Civilsdaily
1700 BC: The Late Harappan and the Early Vedic Period coincide: 1300 BC: The end of the Cemetary H Culture: 1000 BC: Iron Age in India: 1000 BC - 500 BC: Later Vedic Period. Agriculture became the predominant economic activity. There was a change in the political organization and the involvement of people in administration. 600 BC
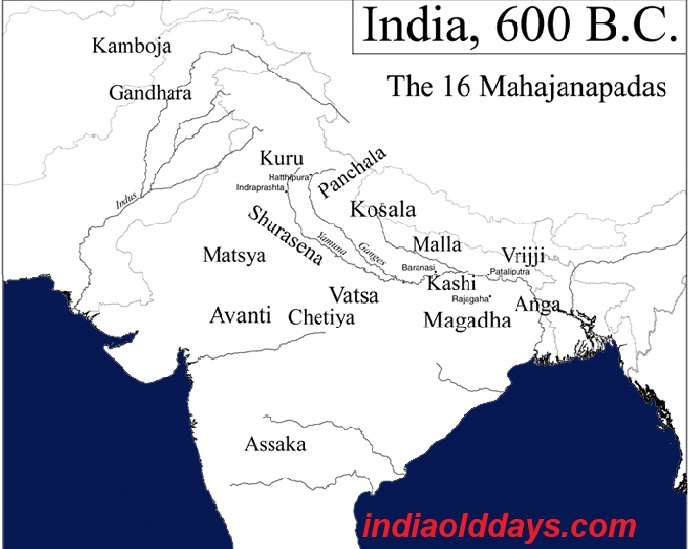
16th Mahajanapad period 600 BC Of India India Old Days
This is a timeline of Indian history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in India and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of India. See also the list of governors-general of India, list of prime ministers of India and Years in India . Pre-historic India

Ancient Maps India Timeline Ramayana Mahabharata History Of India, World History, Art History
600 BC: the Upanishads are composed in Sanskrit 543 BC: Bimbisara of Bihar conquers the Magadha region in the northeast and moves the capital to Rajagriha 543 BC: Chalukya's king Pulakeshin founds a dynasty in Karnataka with capital at Badami/Vatapi 527 BC: prince Siddhartha Gautama is enlightened and becomes the Buddha

The history of Indian map from 600 BC to the 20th century. भारत का प्रथम मानचित्र कैसे बनाया गया
The development of Indian civilization from c. 1500 bce to c. 1200 ce Traditional approaches to Indian historiography The European scholars who reconstructed early Indian history in the 19th century regarded it as essentially static and Indian society as concerned only with things spiritual.

Clash of Worlds A General Overview of Asian History
It is one of the three earliest urban civilizations and made use of an early form of the Indus script, known as Harappan script, for writing purposes. Around 2800 BC, the Kot Diji phase of the Indus Valley Civilization started. Mature Harappan Phase (2600 BC to 1700 BC) The Mature Harappan Phase started around 2600 BC.
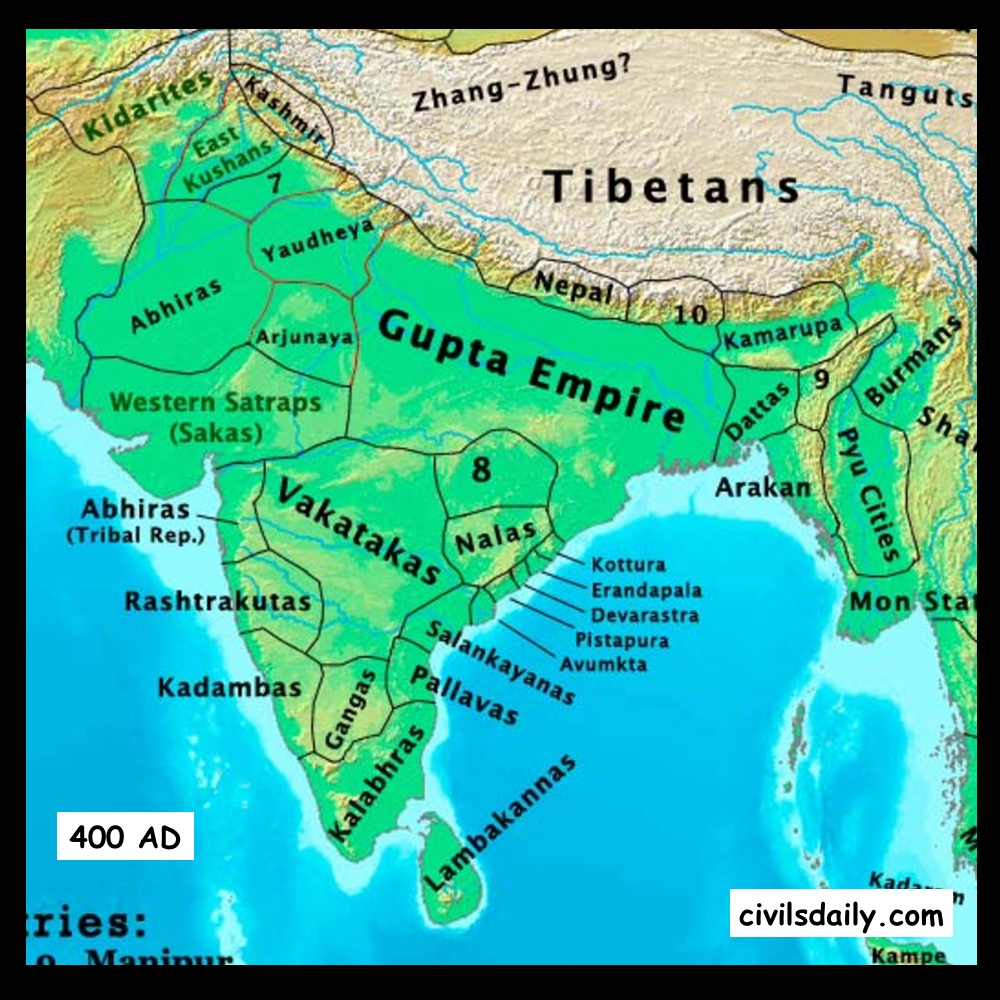
Chapter 7 Gupta Period (300AD 600AD) Civilsdaily
516 BC Darius Invades Indus Valley- In 516 B.C., Darius invaded India capturing the Indus Valley. He annexed it to the Persian Empire. His hold on the region was tenuous and lasted less then ten years. 509 BC The Roman Republic Founded- 509 BC is the year that has traditionally been given as the founding of the Roman Republic. Junius Brutus and.

600 AD Indian history facts, Old maps, India map
World history 6 units · 92 skills. Unit 1 Beginnings - 600 BCE. Unit 2 600 BCE - 600 CE Second-Wave Civilizations. Unit 3 600 - 1450 Regional and interregional interactions. Unit 4 1450 - 1750 Renaissance and Reformation. Unit 5 1750 -1900 Enlightenment and Revolution. Unit 6 The 20th century.

Sixteen Mahajanapada Indian history facts, Indian history, Ancient indian history
The history of India (600 - 187 BC) INDIA'S EARLIEST COINAGE History of India (600 BC - 187 BC) B y the seventh century B.C., Indian settlements extended in a long uneven strip of Panjab to Bihar with a heterogeneous type of population but with enough of a common language and tradition.
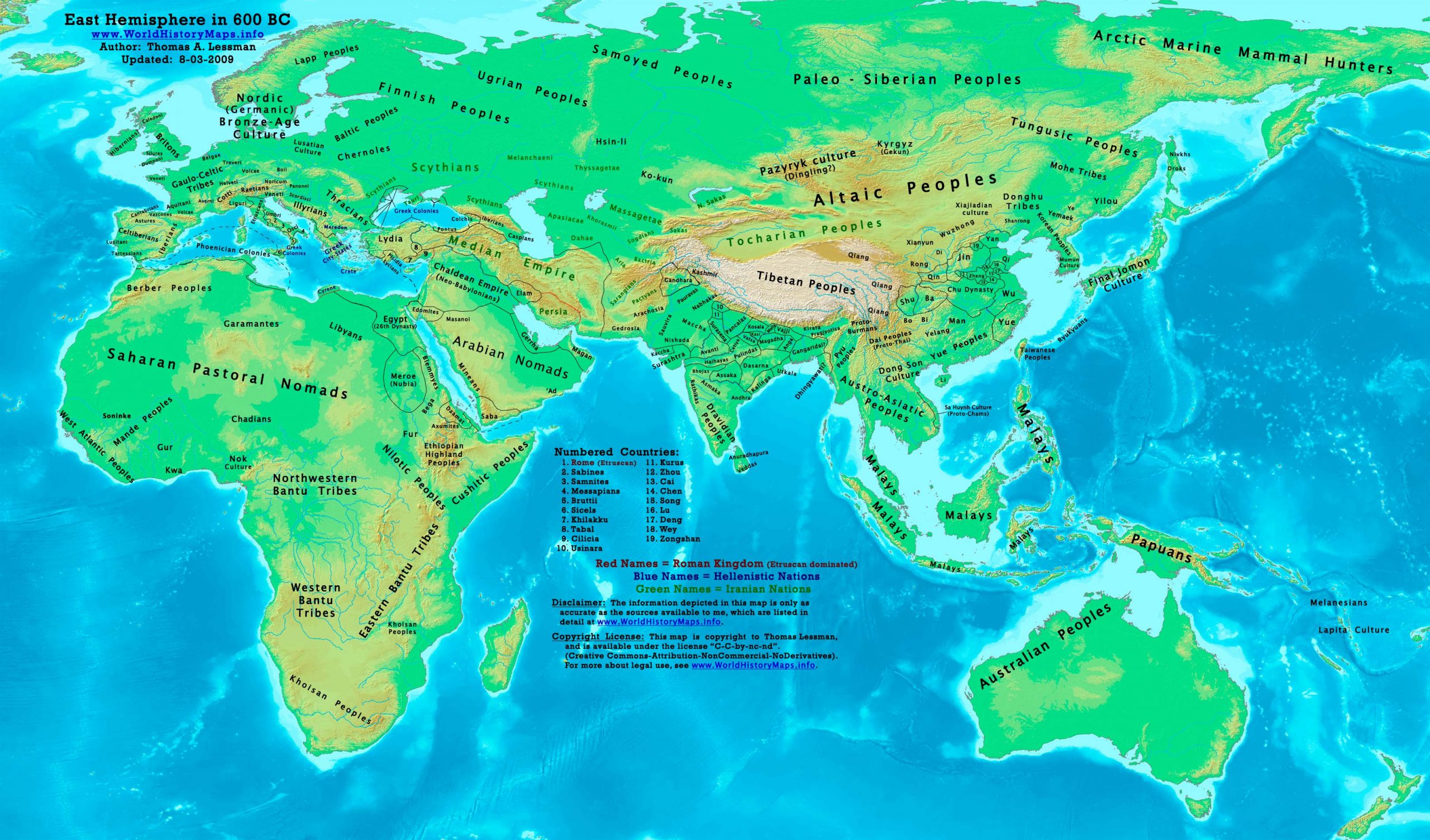
World map 600 BC World History Maps
Human history Human Era ↑ Prehistory ( Pleistocene epoch) Holocene Ancient Postclassical Modern ↓ Future v t e The middle kingdoms of India were the political entities in the Indian subcontinent from 230 BCE to 1206 CE.
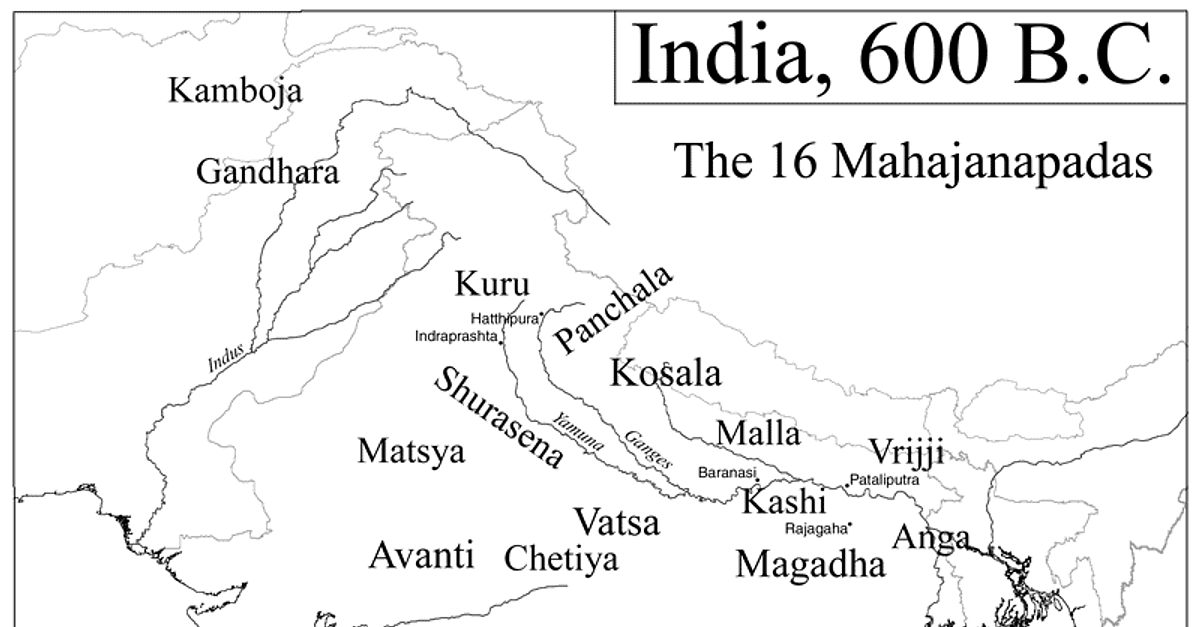
Map of India, 600 BCE (Illustration) World History Encyclopedia
Below we give one or two details of Apastamba's Sulbasutra. This work is an expanded version of that of Baudhayana. Apastamba's work consisted of six chapters while the earlier work by Baudhayana contained only three. The general linear equation was solved in the Apastamba's Sulbasutra. He also gives a remarkably accurate value for √2 namely.
Classical 600 BCE600 CE Noor Khan's History Class
(1500-600 BC) - Black and Red ware culture (1300-1000 BC) - Painted Grey Ware culture (1200-600 BC) - Northern Black Polished Ware (700-200 BC). Seleucid India (312-303 BC) Sangam period (c. 600 BC - c. 300 AD) Pandya Empire (c. 300 BC - AD 1345) Chera Kingdom (c. 300 BC - AD 1102) Chola Empire
Map Of The Gupta Empire unicfirstart
Map of India, 600 BCE Illustration by Kmusser published on 26 April 2012 Download Full Size Image Mahajanapadas ( Sanskrit: महाजनपद, Mahājanapadas), literally "great realms", (from maha, "great", and janapada "foothold of a tribe", "country") were ancient Indian kingdoms or countries.

NOTE BOOKS INDIA Magadha Kingdom 600 BCAD 600
The Republics of Ancient India (600 B.C.-400 A.D.) Article shared by: In the sixth century B.C., we find a large number of states in northern India and many of these were not ruled by kings but formed petty republics or oligarchies.