Codon Anticodon Introduction, Chart & Examples
Approximate Molecular Weight of a Protein. M.W. of protein = # amino acids x 110 Da. Proteins and Amino Acids.

Use your codon chart and tell me what amino acids are coded for by the mRNA sequence AUG CGG UCC
What is a codon? (Definition) A codon is a sequence of 3 molecules/nucleotides describing an amino acid in the sequencing of DNA or messenger RNA (mRNA) or transfert (tRNA). Each nucleotide is described by a letter (among A, C, G, T, U) and the codon can therefore be described by these 3 letters, but also by the name of the amino acid.

Codon tables with the amino acids encoded according to different... Download Scientific Diagram
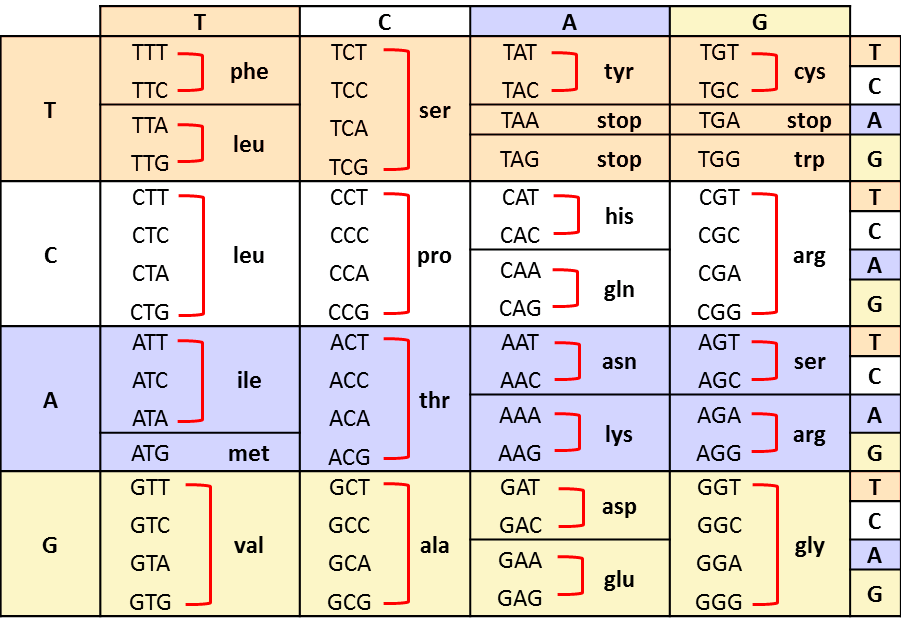
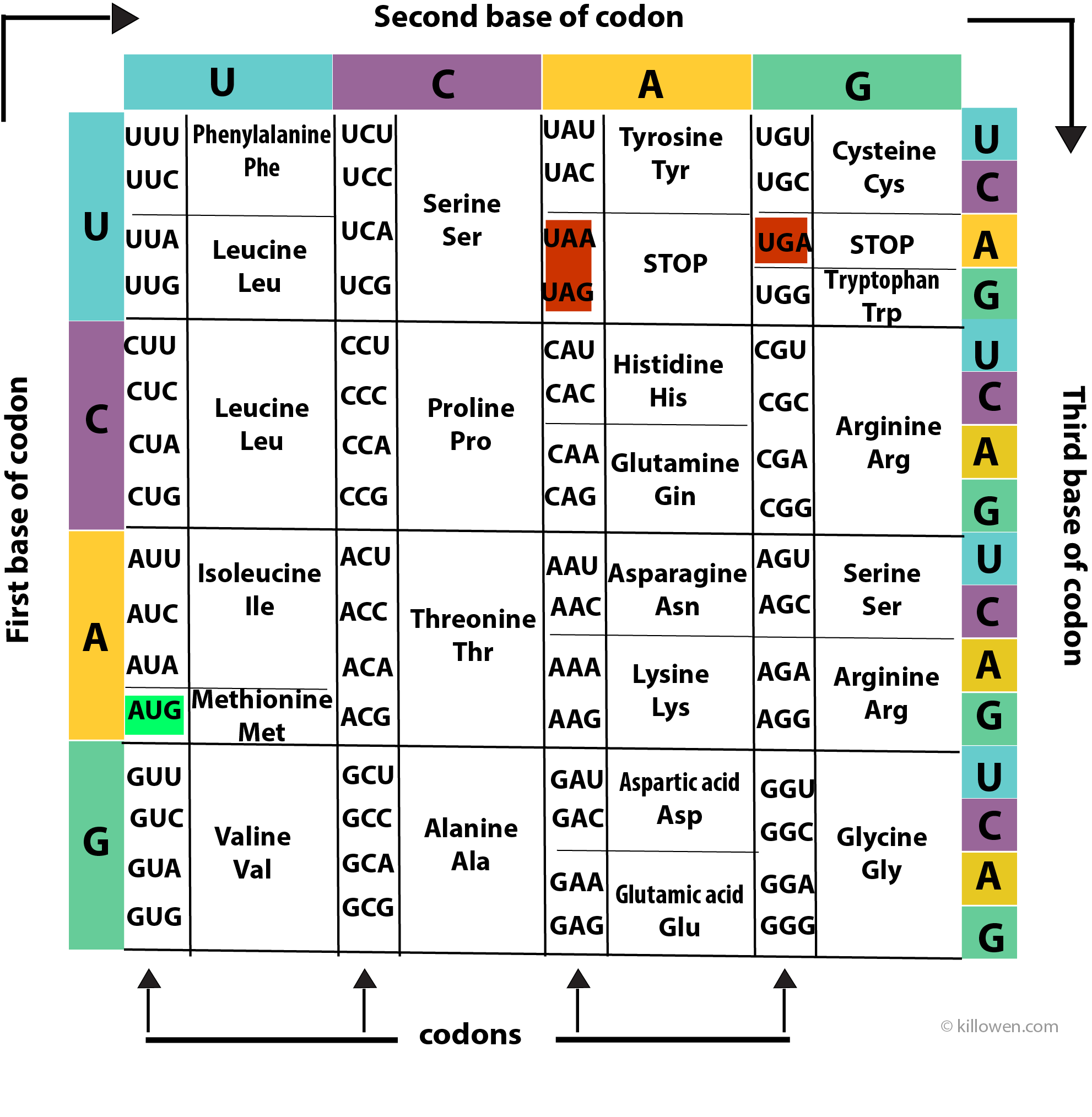
Codons RNA codons designate specific amino acids. The order of the bases in the codon sequence determines the amino acid that is to be produced. Any of the four nucleotides in RNA may occupy one of three possible codon positions. Therefore, there are 64 possible codon combinations.
Amino Acids Coding Structure
mRNA Codon/Amino Acid Chart First Base Second Base U C A G UUU UUC UUA UUG CUU CUC CUA CUG AUU AUC AUA AUG GUU GUC GUA GUG U Phenylalanine (Phe) Leucine (Leu) Leucine (Leu) Isoleucine (Ile) Start Methionine (Met) Valine (Val) UCU UCC UCA UCG CCU CCC CCA CCG ACU
Discovery of a fundamental limit to the evolution of the code IRB Barcelona
There are two steps for making proteins from genes: First, inside the nucleus, a process that makes copies of a certain gene in the form of massager RNAs ( mRNAs ), called transcription. Second, these mRNAs are exported outside of the nucleus to the cytoplasm for ribosomes to make polypeptides/ proteins.

Which codon is the code for the amino acid histidine (His)?
The Genetic Code. The codons are read in the 5´ → 3´ direction. *Termination codons. **AUG start codon. Amino acid reference charts. Includes amino acid structures, peptide bond formation depictions, amino acid abbreviations and molecular weights, the genetic code table.
Amino Acid Codon Chart
Amino acids are the compounds or building blocks that make up peptides and proteins. Each amino acid is structured from an amino group and a carboxyl group bound to a tetrahedral carbon. This carbon is designated as the α-carbon (alpha-carbon). Amino acids differ from each other with respect to their side chains, which are referred to as R groups.
Why a Triplet Code? Gene Expression Part 1 Reading Genes to Make Proteins passel
Figure 2.3. 3: A codon table shows the amino acid specified by each codon. The codon AUG is the start signal for translation which places the amino acid, methionine (Met) at the beginning of each protein. Three codons, UAA, UAG, and UGA, called stop codons, act as signals to terminate translation.

RNA to Protein Translation in PERL BioGem Blog
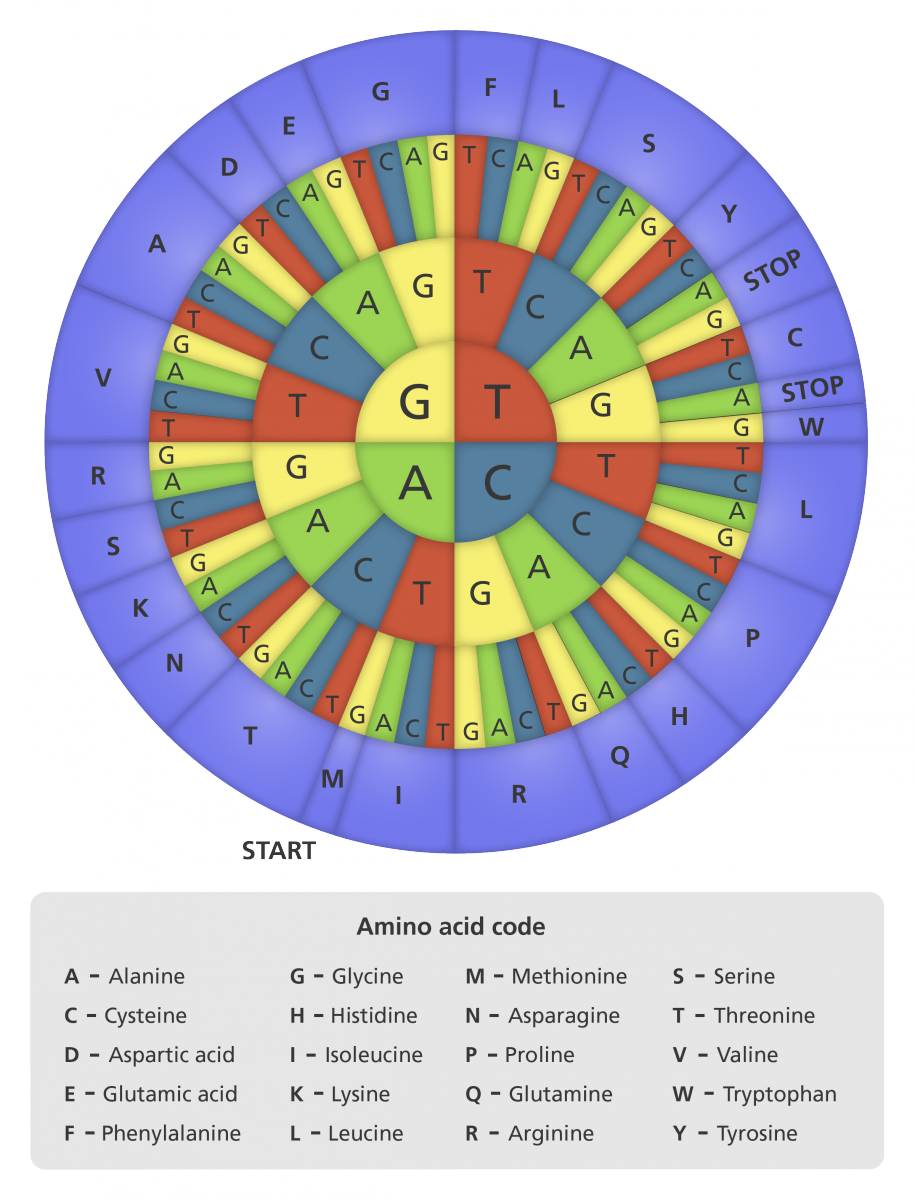
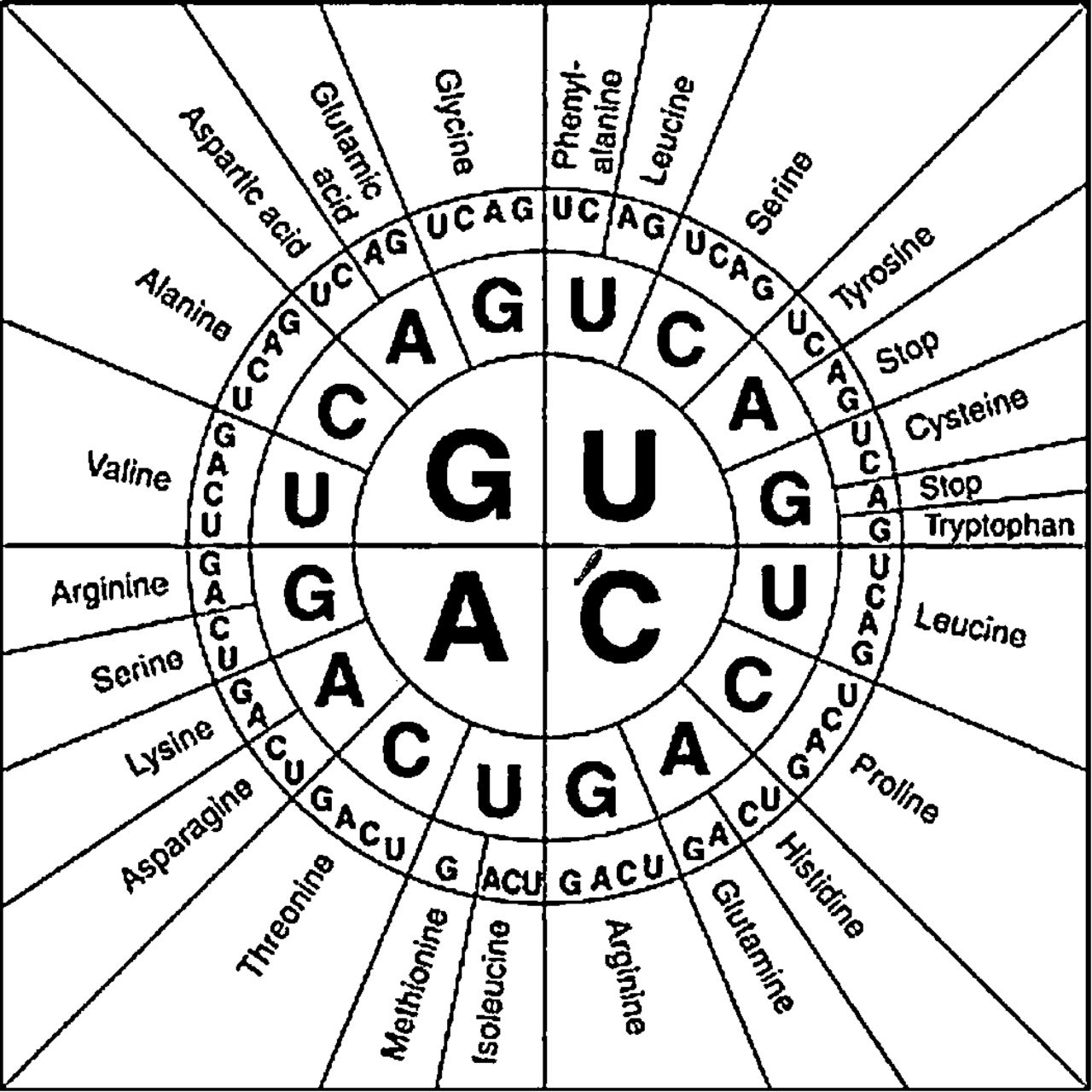
The complete set of correspondences between codons and amino acids (or stop signals) is known as the genetic code. [Codon table] → → → → In the rest of this article, we'll more closely at the genetic code. First, we'll see how it was discovered.
[Solved] b) Use the codon table below to find the first three amino acids in... Course Hero
Most codons specify an amino acid Three "stop" codons mark the end of a protein One "start" codon, AUG, marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine
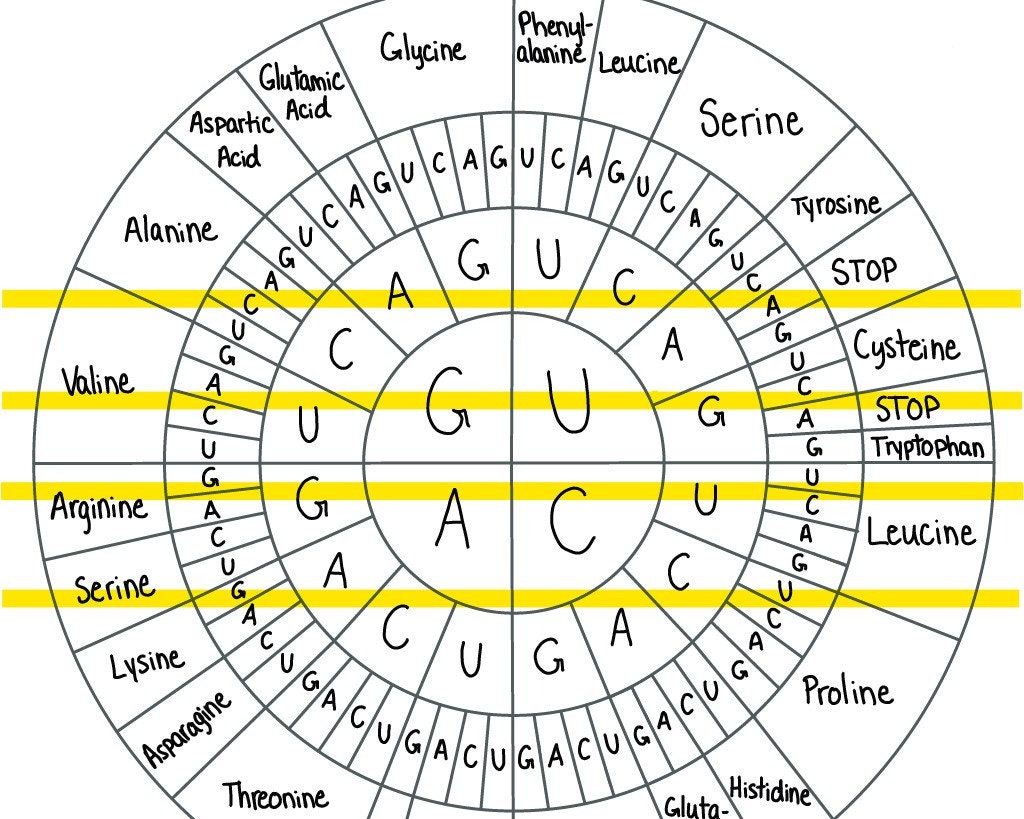
Amino Acid Codon Chart Template Etsy
genetic code amino acid descriptions - one / three letter code amino acid properties PAM-matrix Genetic code NOTE - starting VarNomen version 3 the '*' is used to indicate a translation stop codon, replacing the 'X' used previously (see Background). Amino acid descriptions Amino acid properties
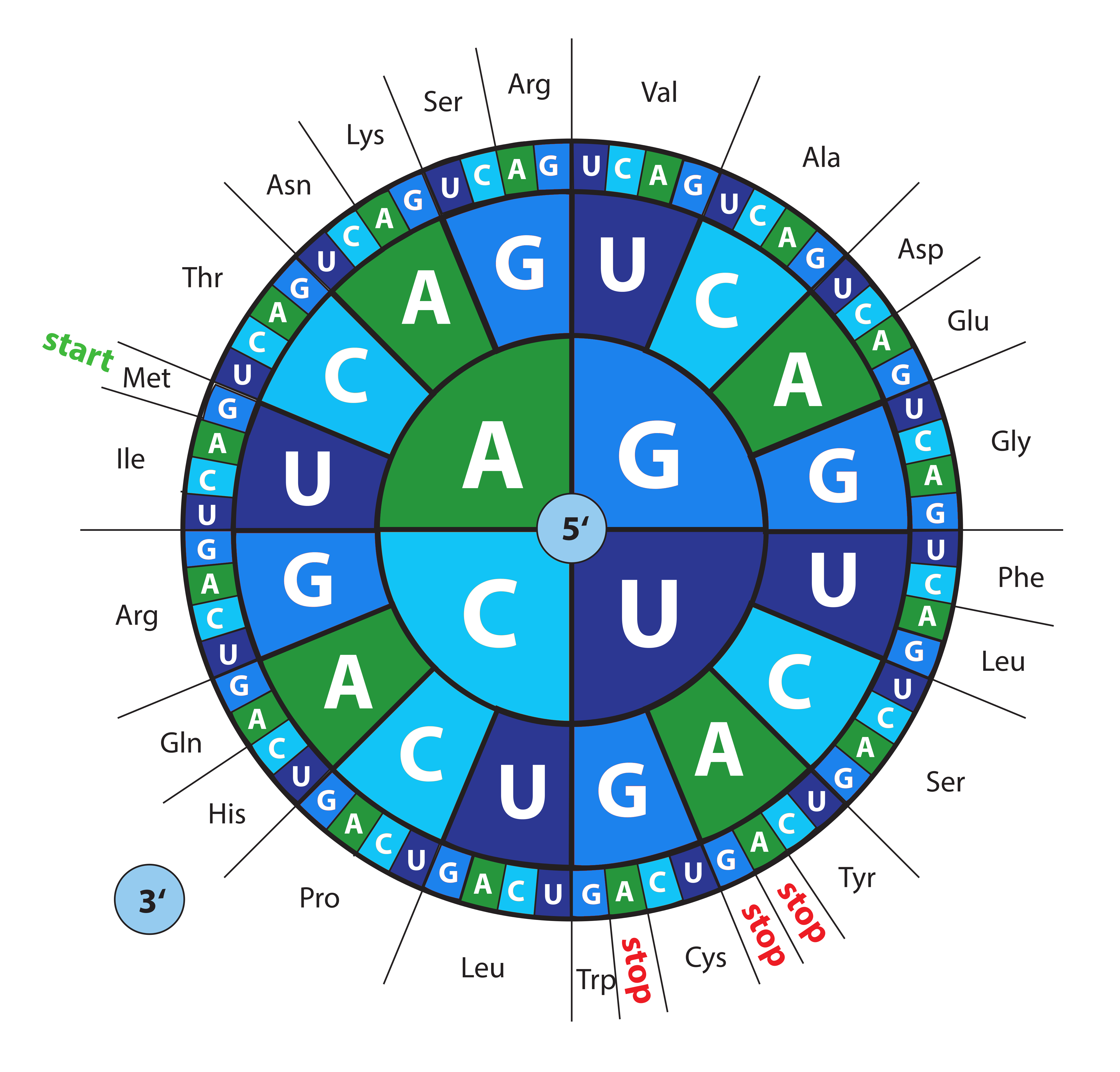
Blue Heron Biotech, LLC Gene Synthesis Codon Optimization
The remaining 61 codons specify the 20 amino acids that make up proteins. The AUG codon, in addition to coding for methionine, is found at the beginning of every mRNA and indicates the start of a protein. Methionine and tryptophan are the only two amino acids that are coded for by just a single codon (AUG and UGG, respectively). The other 18.
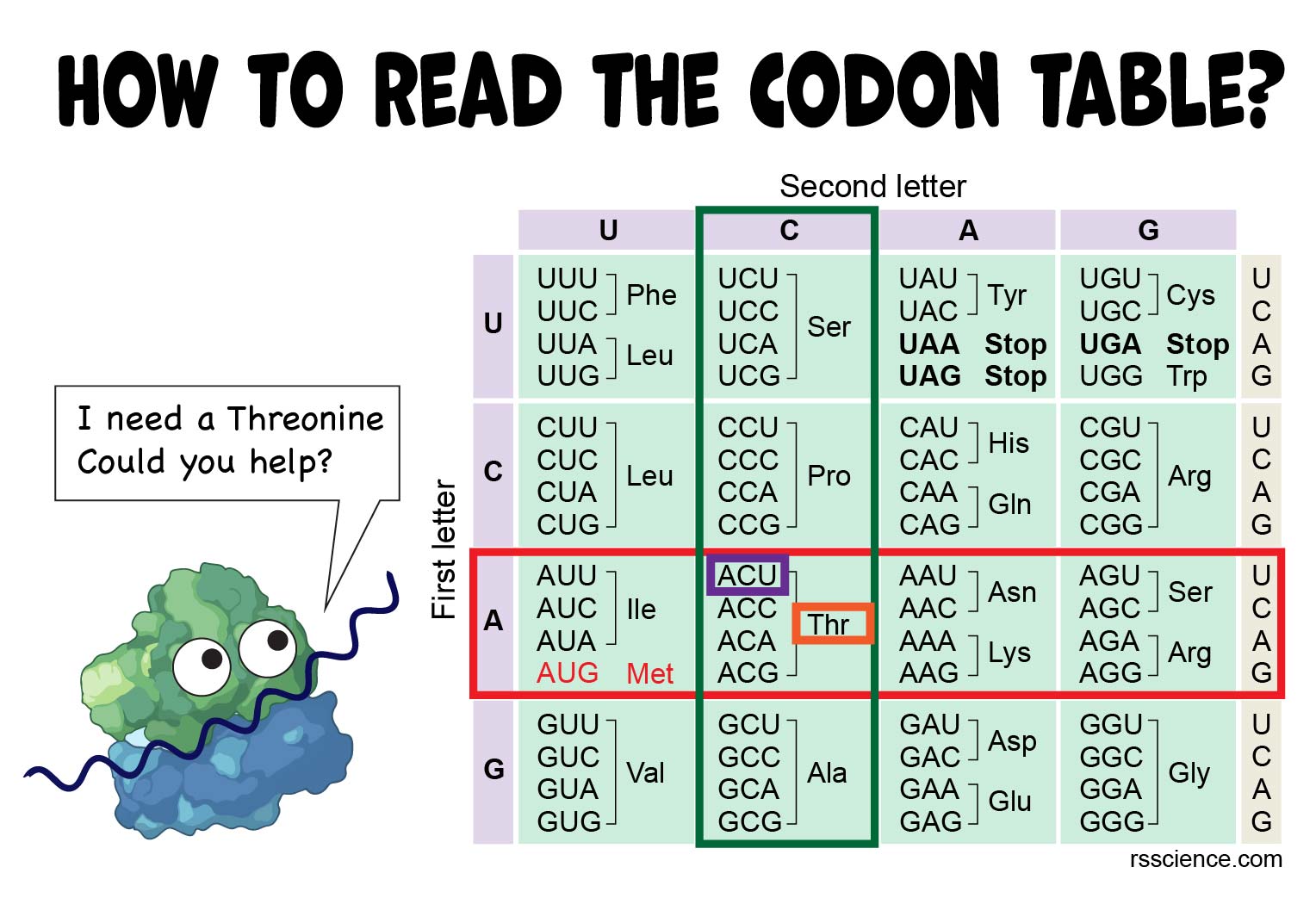
How to Read the Amino Acids Codon Chart? Code and mRNA Translation Rs' Science
A series of codons in part of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Each codon consists of three nucleotides, usually corresponding to a single amino acid. The nucleotides are abbreviated with the letters A, U, G and C. This is mRNA, which uses U ( uracil ). DNA uses T ( thymine) instead.

Protein Synthesis (Translation) Microbiology
The codes are universal irrespective of the type of organism, i.e. CGU would code for Arginine in animals as well as in bacteria, but exceptions exist. Out of 64 codons, 3 are stop codons which do not code for any amino acids and thus end the process of translation. AUG coding for Methionine is the only codon that acts as an initiator codon.

The classic circular code Download Scientific Diagram
The upper axis refers to the second letter of the codon, so we find A along the upper axis. This tells us the column of the table in which our codon will be found. The row and column from steps 1 and 2 intersect in a set of boxes in the codon table, one half containing four codons and the other half containing the mapped amino acid(s).
[Solved] Using the codon chart, determine both the mRNA and amino acid... Course Hero
A codon chart or table is used as a reference tool that correlates specific codons with the corresponding amino acids they encode. Codon Chart and Codon Table The chart helps to decipher the genetic code and understand which amino acids are synthesized based on the sequence of nucleotides. In total, there are 64 possible codons.