PPT Introduction to Fungi PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2001302
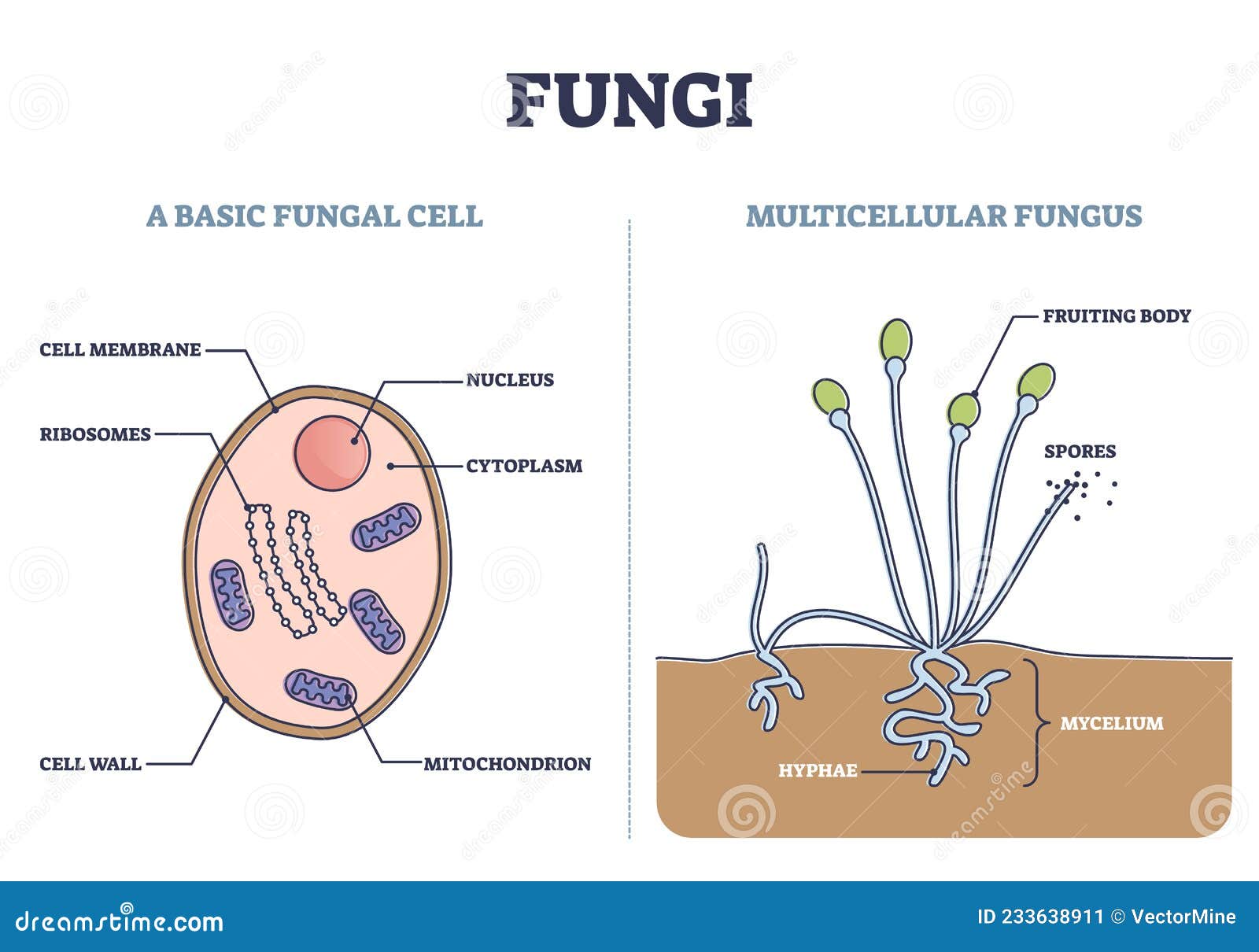
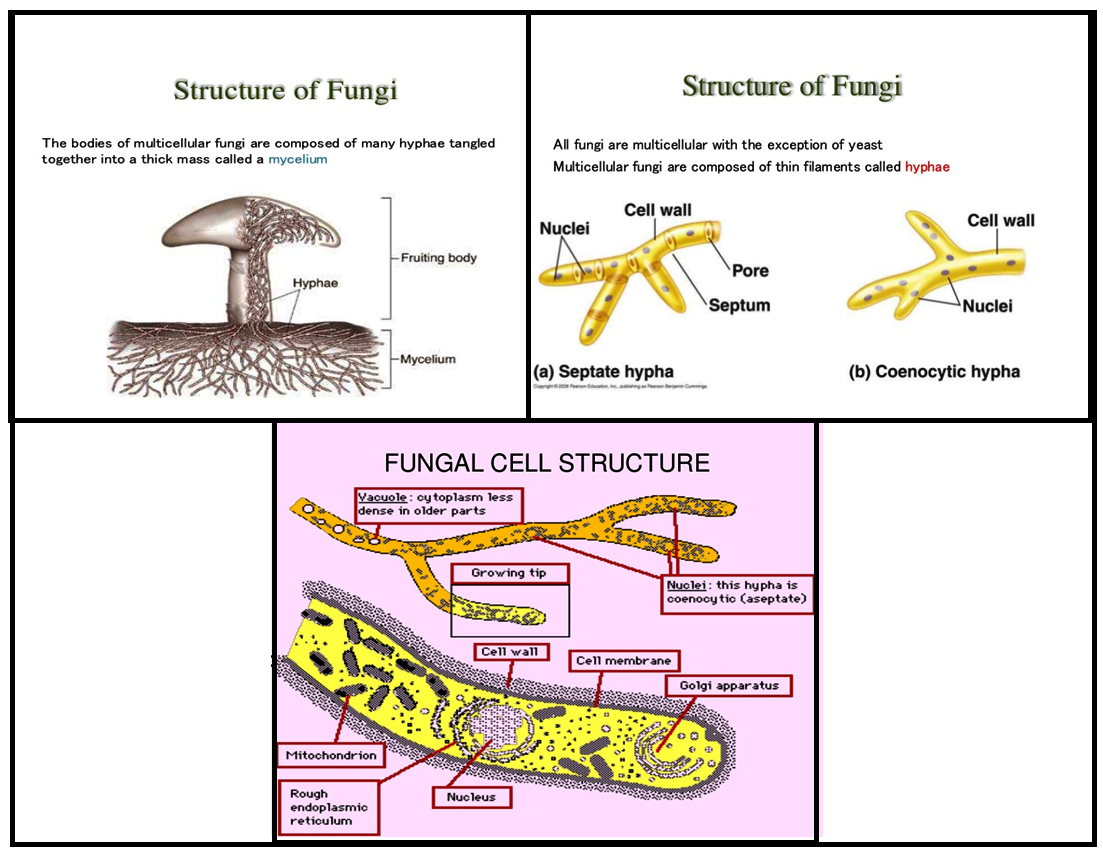
Structure of Fungal Cell (With Diagram) | Fungi Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the structure of fungal cell. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of the fungal cell. (a) The Cell Wall of the Fungal Cell:
Fungi. Classification Based on Cell Division Stock Vector Illustration of human, multicellular
24.1 24.1 Characteristics of Fungi Highlights Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: List the characteristics of fungi Describe the composition of the mycelium Describe the mode of nutrition of fungi Explain sexual and asexual reproduction in fungi
Fungi Structure Diagram
Human pathogenic fungi produce three basic 'cell' types: hyphae, yeast cells, and spores. The organization and subcellular structure of these different cell types and their modes of growth and formation are reviewed. Growth and form is the consequence of how new cell surface is formed.
Eukaryotic Organisms Fungi & Protoctists Gidemy Class Notes
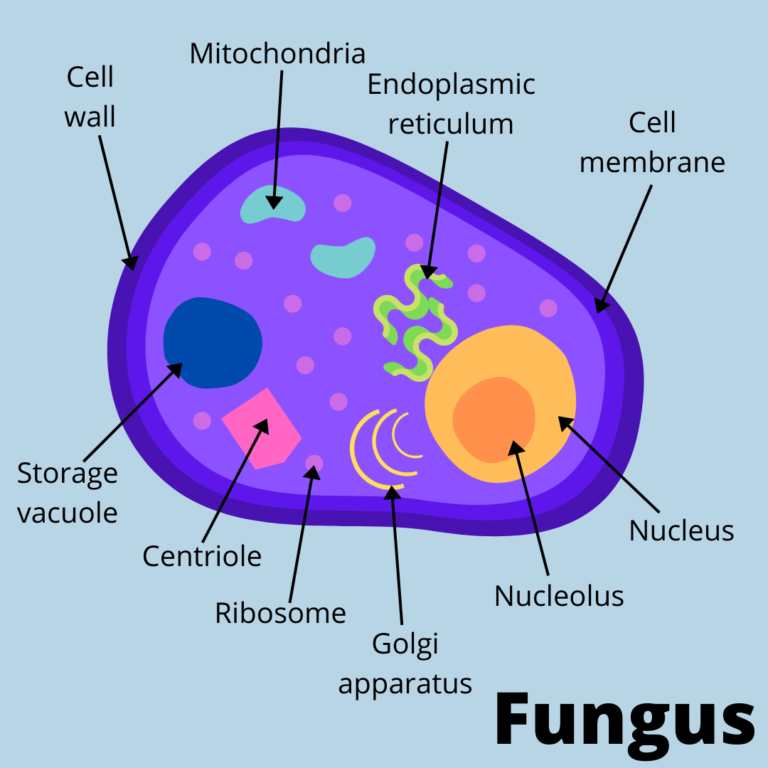
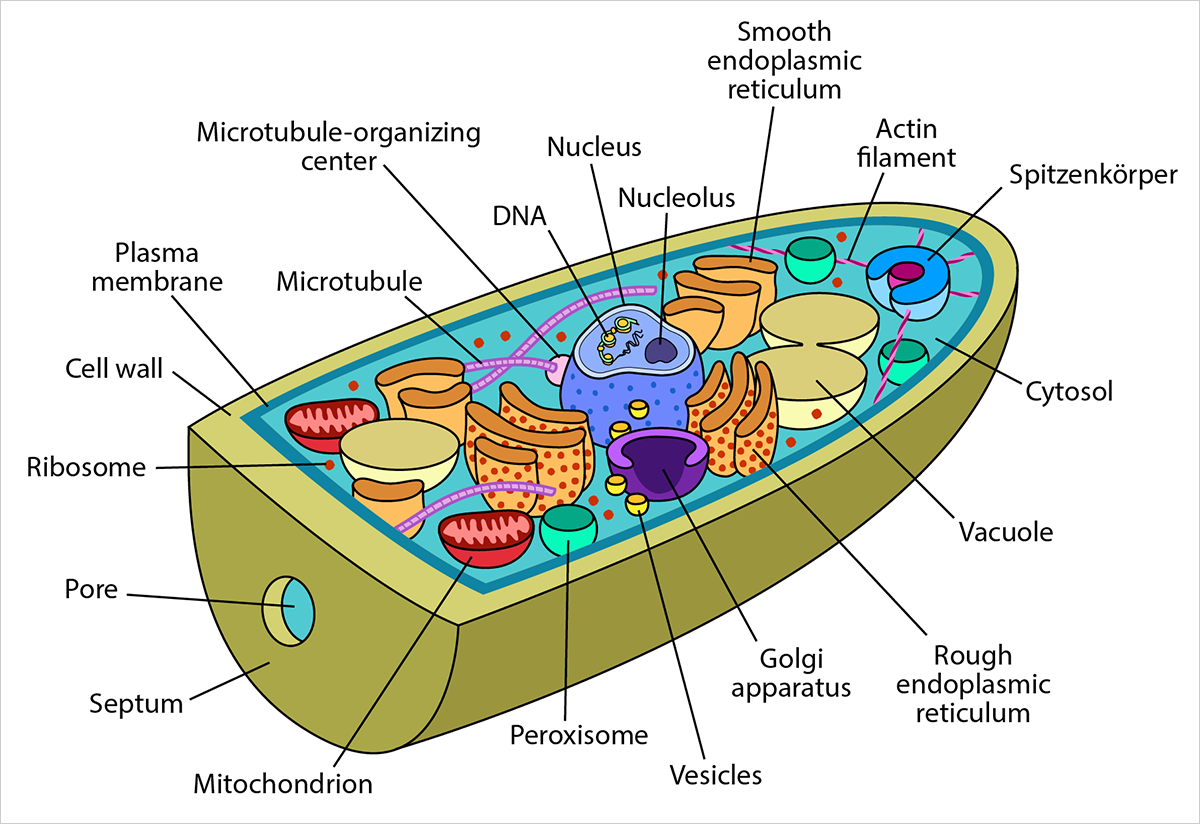
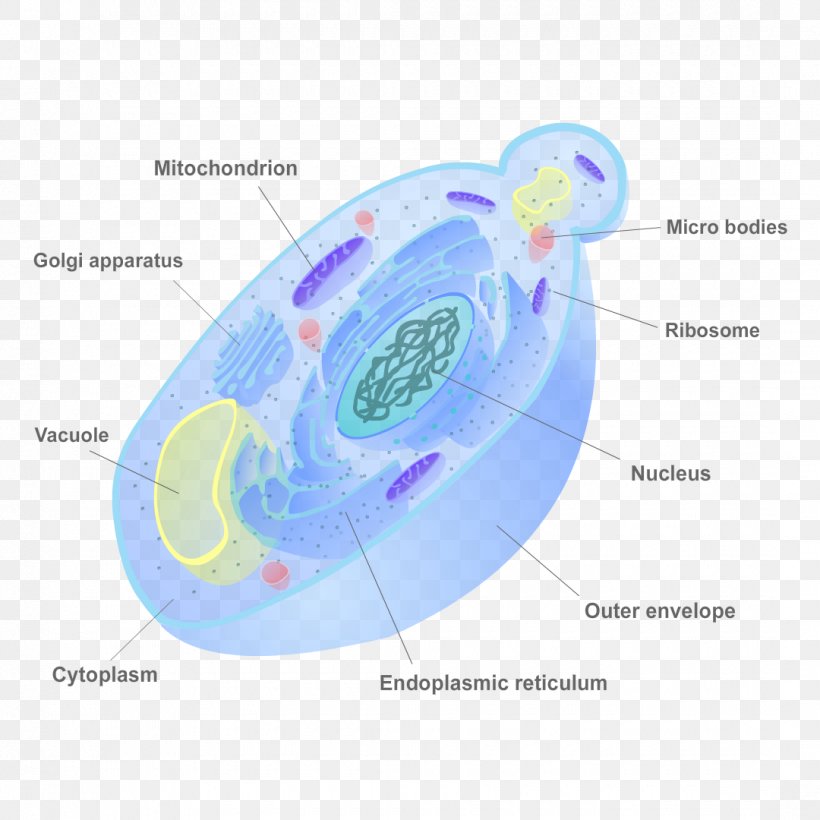
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes and have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus where the DNA is wrapped around histone proteins. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of DNA). Fungal cells also contain mitochondria and a complex.

Fungi (Importance, Classification and More) Solution Pharmacy
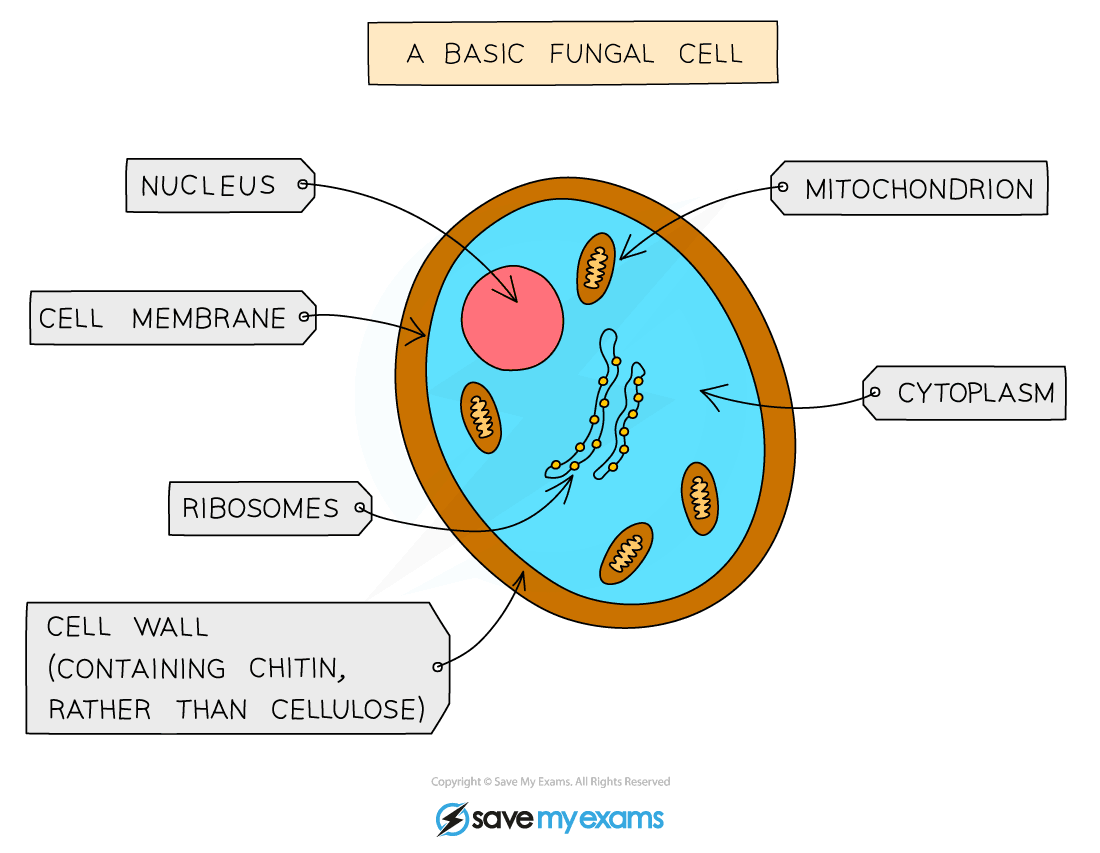
The cell wall is a characteristic structure of fungi and is composed mainly of glucans, chitin and glycoproteins. As the components of the fungal cell wall are not present in humans, this structure is an excellent target for antifungal therapy.

Fungi Cell Stock Illustration Download Image Now Hypha, Fungus, Biological Cell iStock
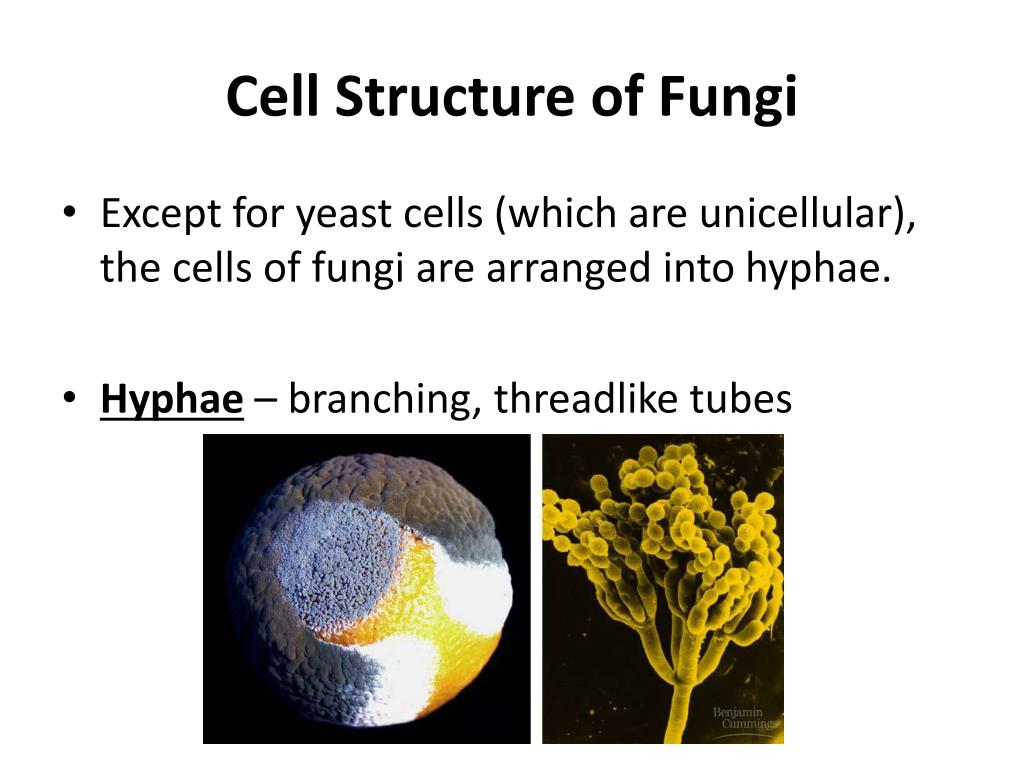
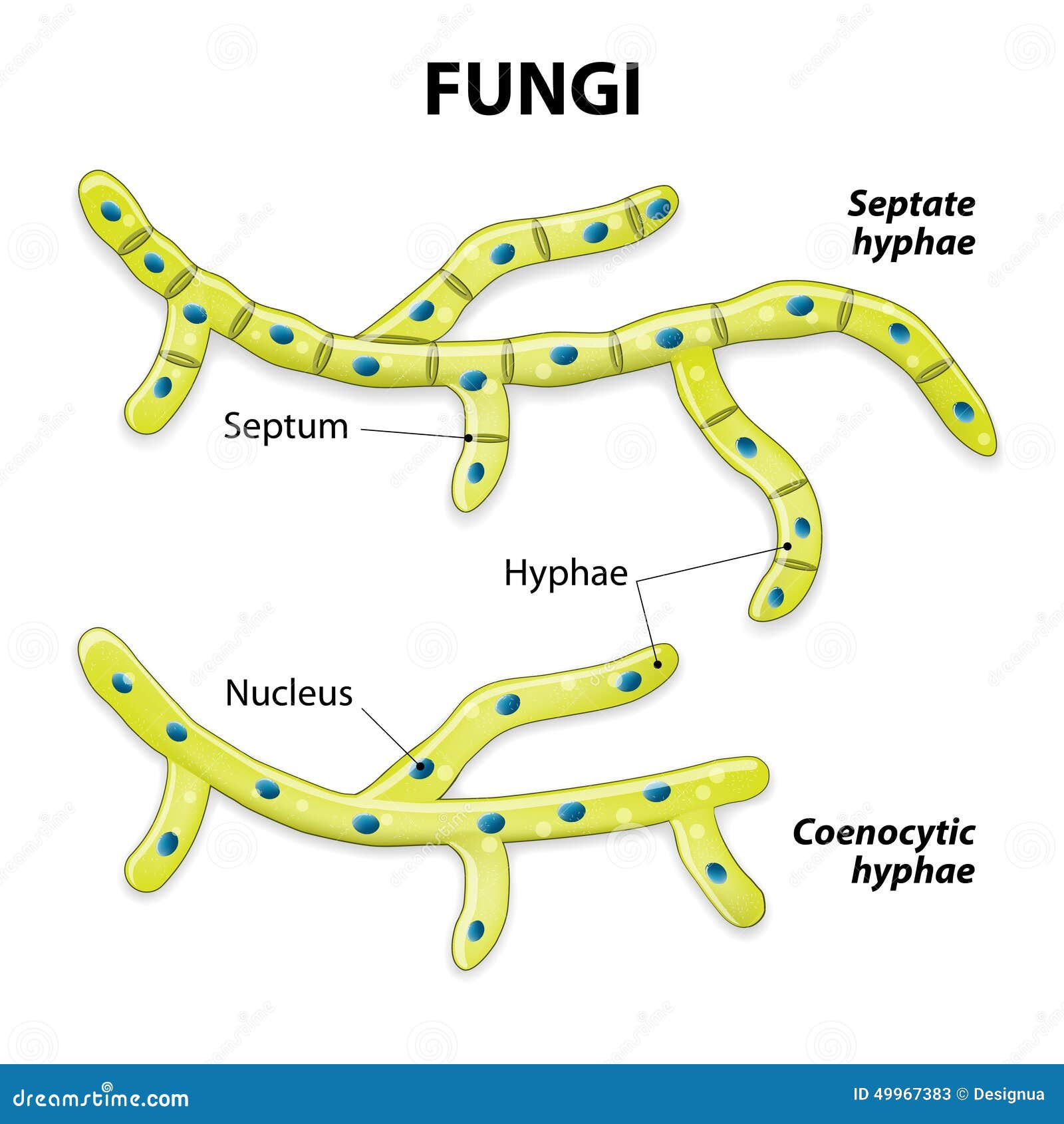
A typical fungus consists of a mass of branched, tubular filaments enclosed by a rigid cell wall.The filaments, called hyphae (singular hypha), branch repeatedly into a complicated, radially expanding network called the mycelium, which makes up the thallus, or undifferentiated body, of the typical fungus.The mycelium grows by utilizing nutrients from the environment and, upon reaching a.
Cell Anatomy Deviche Designs
Biology Cells Fungi Cell Fungi Cell Explore the complex world of microbiology with an in-depth look at fungi cell structures. This detailed analysis includes examination of key components, distinctive features and an intricate fungi cell diagram.
Fungus Cell Wall Yeast Biology, PNG, 1080x1080px, Fungus, Biology, Cell, Cell Wall, Chitin
Cell Structure and Function Fungi are eukaryotes and as such have a complex cellular organization.
Fungi As Basic Fungal Cell and Multicellular Fungus Structure Outline Diagram Stock Vector
In this context, we will discuss the structure of fungi by looking into the diagram and morphological features of both yeasts and moulds. Content: Fungal Cell Structure Characteristics Ultrastructure Structure of Yeasts Structure of Molds Distinguishing Characteristics of Fungi Fungal cells show resemblance to both plant and animal cells.

Kingdom Fungi In Detail Biology Blog
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes, and as such, have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. The DNA in the nucleus is wrapped around histone proteins, as is observed in other eukaryotic cells. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of.

Morphology
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes and as such have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to the plasmids (loops of DNA) seen in bacteria. Fungal cells also contain mitochondria and a complex system of internal membranes.

Science Class 5EP
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes, and as such, have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. The DNA in the nucleus is wrapped around histone proteins, as is observed in other eukaryotic cells. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of.

Fungal cell pictures
The composition of fungal cell walls is relatively simple and includes substances not typically found in animal and plant hosts (e.g., chitin). On this basis, it may be possible to identify pathogen-specific molecular targets from investigations of the biosynthesis of fungal wall components.

Types of Cells Biology Dictionary
A fungus ( pl.: fungi [2] or funguses [3]) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae and either Protista [4] or Protozoa and Chromista. [5]
Biology KINGDOM FUNGI
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes, and as such, have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. The DNA in the nucleus is wrapped around histone proteins, as is observed in other eukaryotic cells. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of.
PPT Lab 10. Overview PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4944026
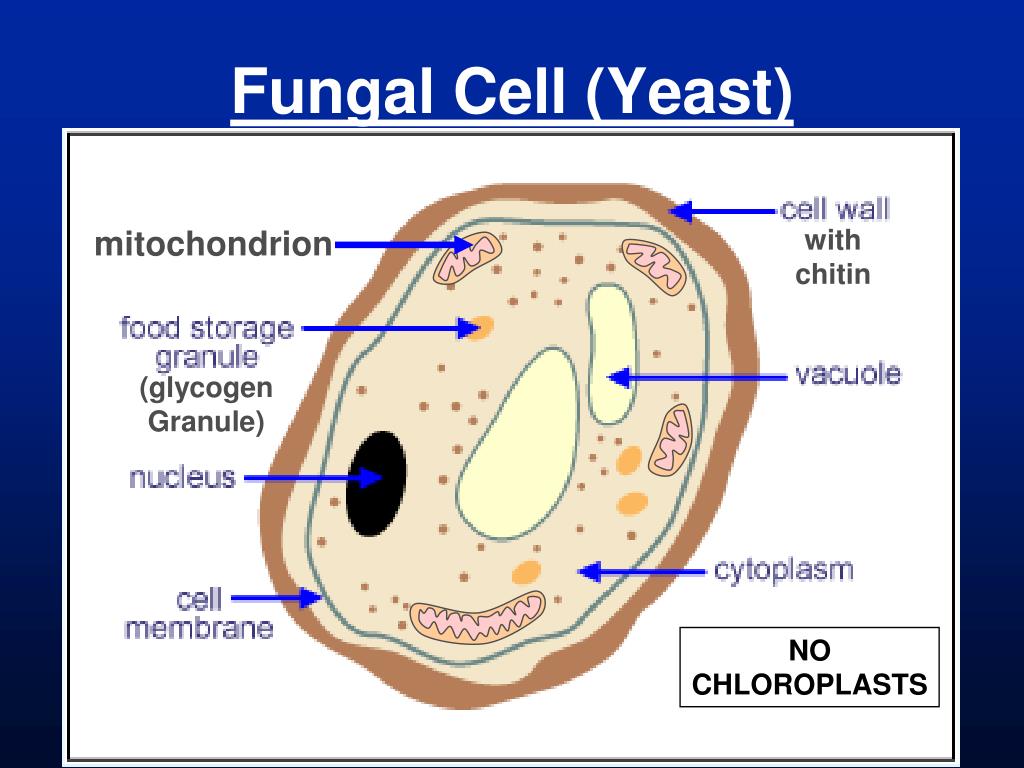
The diagram below shows the ultrastructure of a typical yeast cell: Bacterial cells Bacterial cells have a more simple structure compared to animal, plant and fungal cells and are.